Measuring the Surface Resistance of Industrial Materials
What is static electricity?
Static electricity is an imbalance between negative and positive charges in objects. Charge remains until it is able to move away through electric current or discharge through another object. One spectacular example found in nature is lightning. Static electricity has contributed to the invention of products used daily such as supercapacitors, laser printers and paint spray guns. While static is useful, it can also be a nuisance, causing painful shock and damage to delicate electronics. In extreme cases, it can lead to danger such as explosions in hazardous zones.

IEC Standard 60079-0 for Surface Resistance Testing
According to the IEC standard 60079-0, equipment that contains non-metallic materials as enclosures is required to have its surface resistance tested. The test is conducted on parts of the enclosure or a test piece in accordance to the specified dimensions. The test object has to be conditioned at least 24 hours at 23°C and 50% relative humidity and also tested in the same ambient conditions. A direct 500 V will be applied for 65 seconds between 2 electrodes. The surface resistance will then be measured. The typical value of the surface resistance is between 106 to 1012 Ω. A high surface resistance value indicates that the material is more insulative.
Critical Environments that Require Surface Resistance Testing
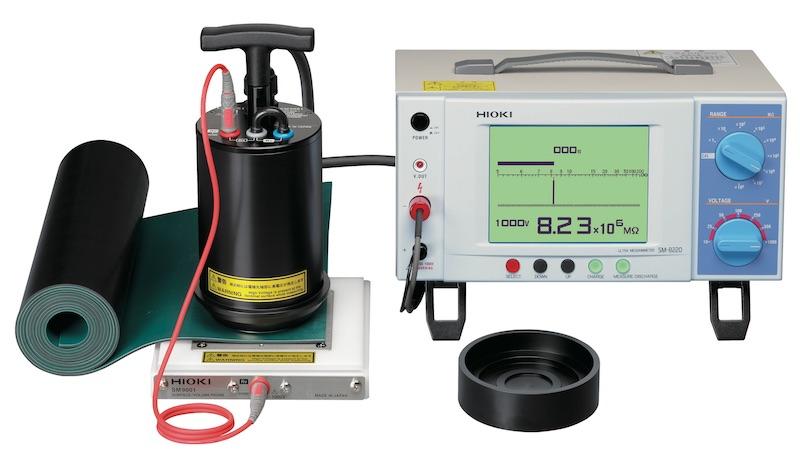
In critical environments such as hospital operating rooms where sensitive electronic equipment is used, stringent static control is required. Furthermore, compressed oxygen is often used in the room. A small discharge has the potential of disturbing the sensitive electronic components resulting in the malfunction of equipment and causing fire hazards due to the compressed oxygen. To address this, electrostatic discharge (ESD) measures are put in place to prevent the buildup for static electricity. Static dissipative ESD flooring is also used. Other preventive measures include humidity control of the operating room and use of static-controlled clothing and footwear. In order to be ESD safe, the flooring material is tested in accordance to IEC61340-2-3 (Part 2-3: Methods of test for determining the resistance and resistivity of solid materials used to avoid electrostatic charge accumulation).
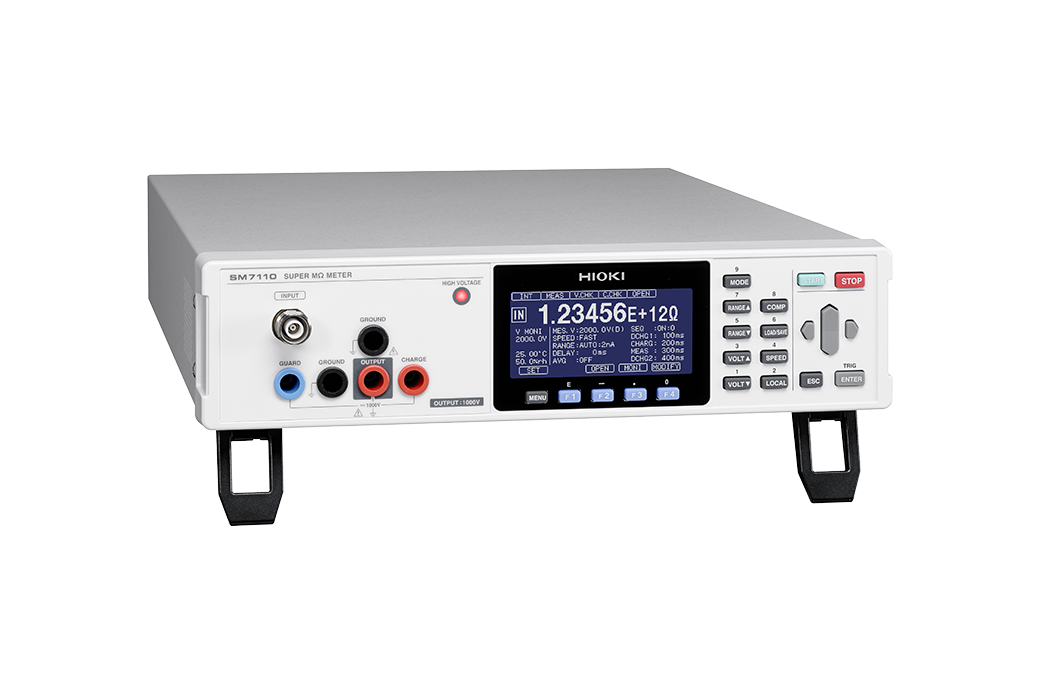
A Solution in the Hioki SM7110 Super Megohm Meter
A super megohm meter (also known in industry as an electrometer or picoammeter) such as the Hioki SM7110 is used to measure the surface resistance of materials. The SM7110 can perform simultaneous measurement of temperature and humidity. This is important when conducting measurement and managing new materials as changes in either can affect the insulation resistance.
The sequence mode feature of the SM7110 enables the user to set the time for “Discharge – Recharge – Measurement –Discharge” flow and perform repeated measurements without the use of a computer. Various electrodes and shield boxes are available to cater to different applications. For example, the SM9001 Surface/Volume Resistance Measurement Electrode (shown below) is compliant to IEC61340-2-3 standards, making it suitable for measuring anti-static flooring materials. Measurements can be conducted easily as no cutting of samples is required. This is because the electrode uses a conductive rubber where the size conforms to standards. Hence, only the electrode needs to be place on the desired point for stable measurements under the load of 2.5 kg.

Advantages of the SM7110
The SM7110 delivers strong resistance against noise, giving a high stability which is crucial for high resistance measurement. It also provides a management range up to 2 x 1019 Ω. With the capability to give reliable readings and the availability of various accessories, the SM7110 is ideal for accomplishing the task of testing the resistance of surface material in order to ensure a safe industrial environment.



