Testing of Dielectric Constant and Dielectric Loss Tangent Temperature Characteristics in Electrical Insulating Materials
Demand is growing for the ability to test the dielectric constant and dielectric loss tangent of electrical insulating materials used in EV and power electronics applications in high-temperature environments. Measurement electrodes from KEYCOM can be combined with Hioki’s LCR meters to meet this need.
Target
• Electrical insulating materials, including flat plates (solids), liquids, gels, sheets, and films
• Ceramics, laminated boards, plastics and resins, insulating paper, etc.
• R&D and production testing
Highlights
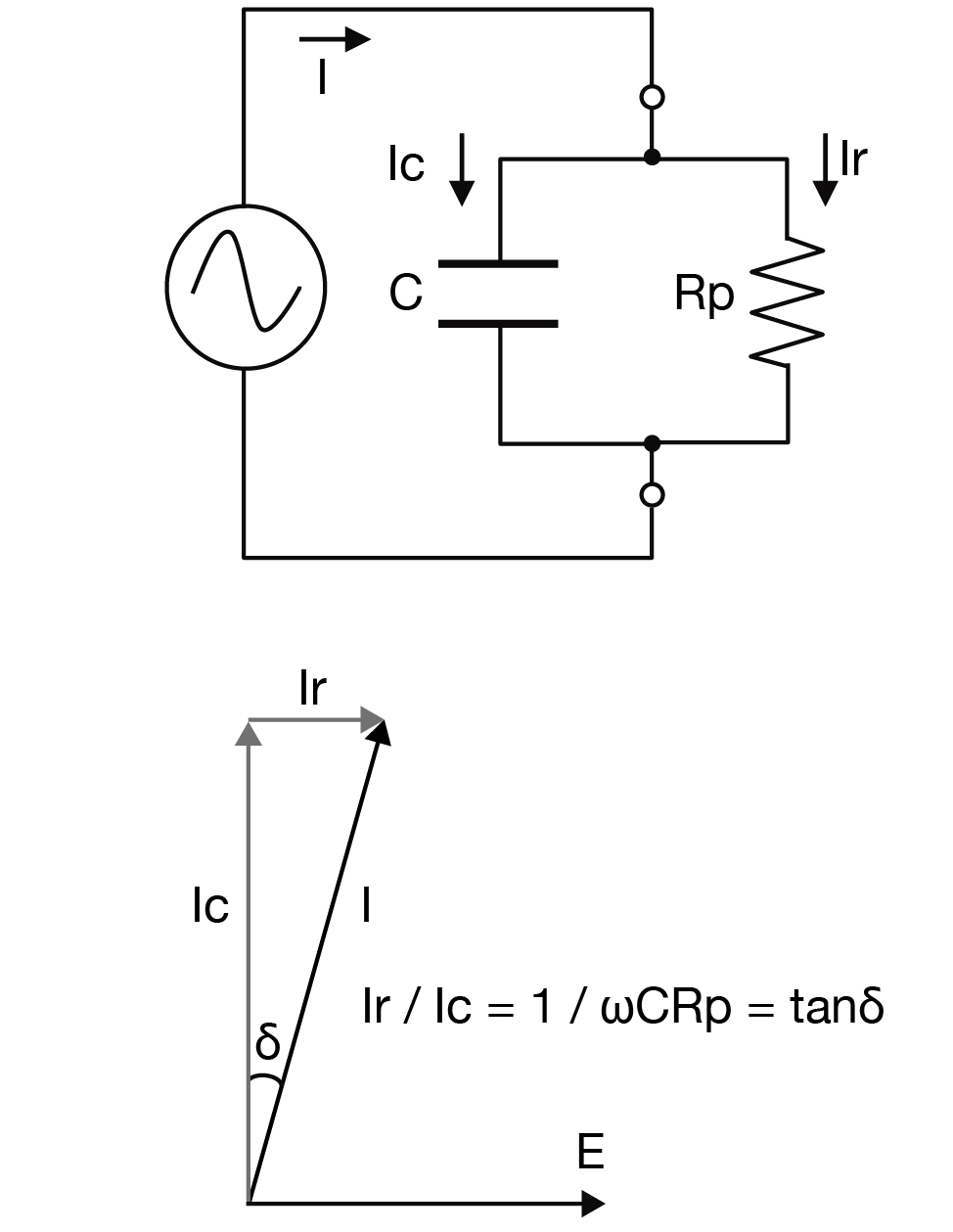
The dielectric loss tangent δ serves as a quantitative indicator of the state of an electrical insulating material. When an AC voltage is applied to an insulator, dielectric loss (or dissipation loss) occurs, causing some of the electrical energy to be lost as heat energy. The dielectric loss tangent, which indicates the extent of this loss, is dependent on the applied AC frequency, temperature, and humidity.
Switched voltages are applied to electrical insulating materials used in inverters, converters, and motors. Consequently, it is essential to test tan δ at the appropriate switching frequency. In addition, testing of the tan δ-temperature characteristics of electrical insulating materials is important since EV motors and power modules can be expected to be used in environments that range from low temperatures to temperatures in excess of 200°C.
Problem
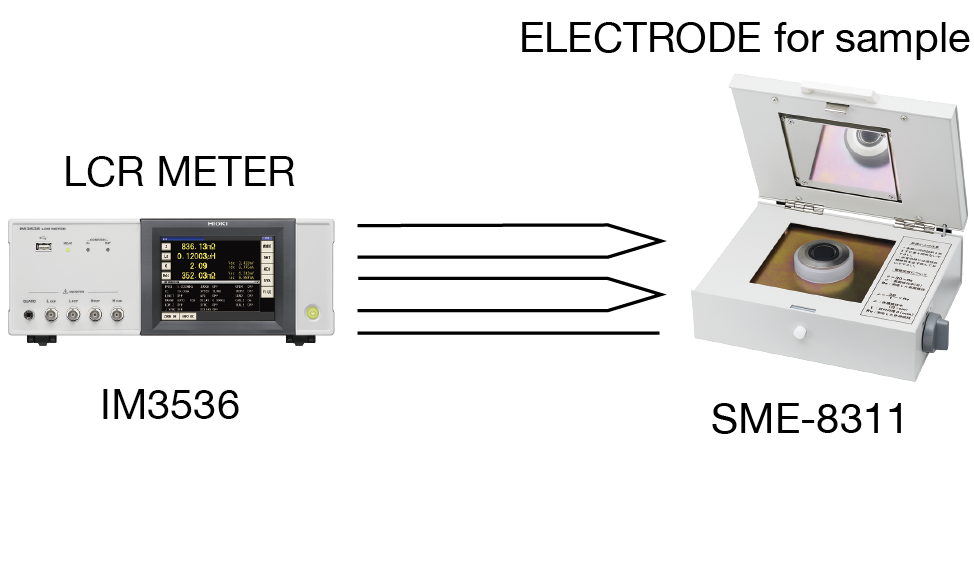
Sample electrodes consisting of a primary electrode and counter-electrode are used to measure tan δ when measuring high-impedance elements such as electrical insulating materials. These electrodes combine a card electrode that’s designed to reduce the effects of stray capacitance and inductive noise with a shielding mechanism.
Since dielectric loss tangent and insulation resistance measurement of standard electrical insulating materials, for example under the JIS C 2138 or IEC 60250 standard, use a test environment temperature of 20°C or 23°C, an LCR meter and sample electrode can be used to conduct standard-compliant tests. However, sample electrodes may not be able to withstand test temperatures under protocols such as ASTM D150, which tests temperature dependence.
Solutions
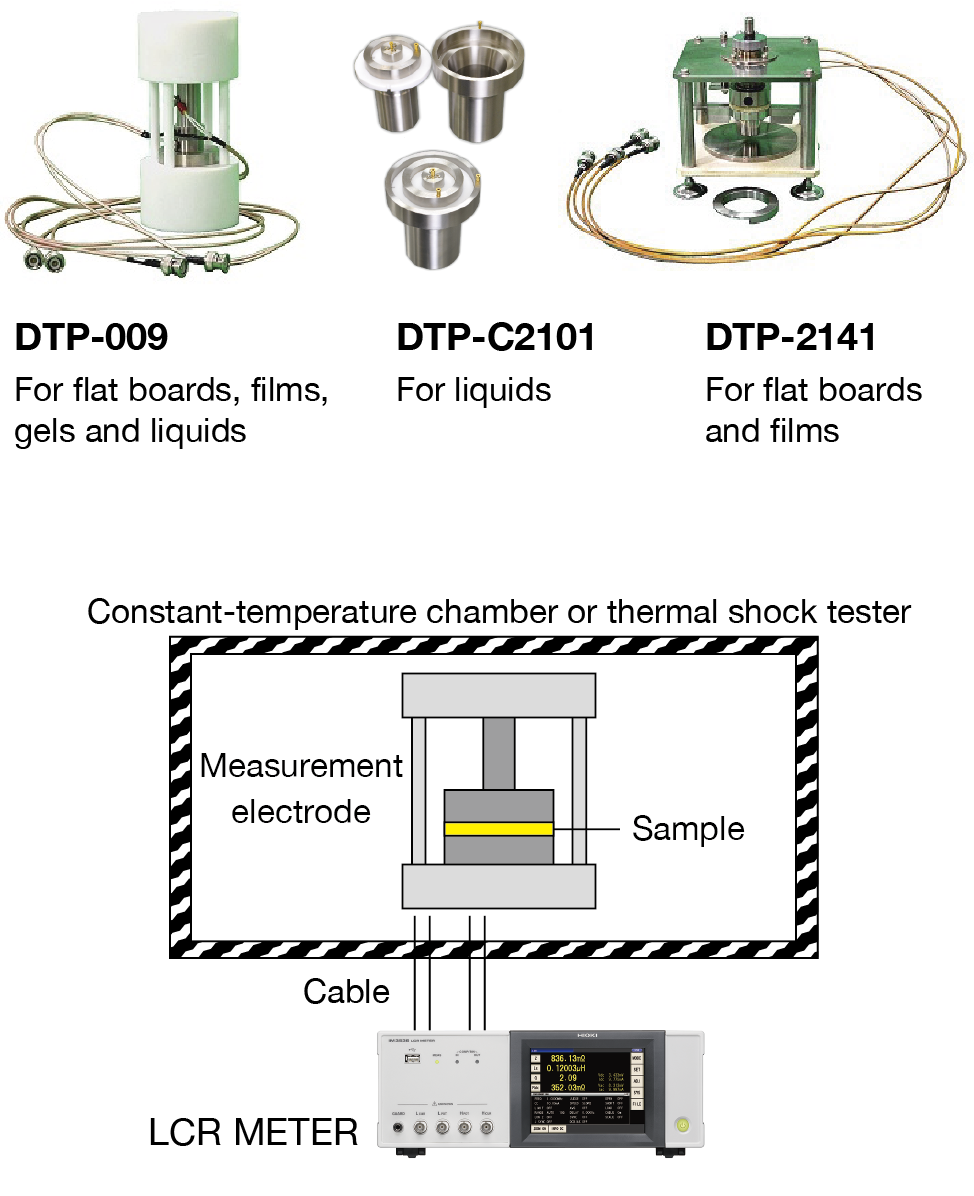
Capacitive electrodes for measuring dielectric constant and dielectric loss tangent from KEYCOM (https://www.keycom.co.jp/ndex-j.html) make possible tan δ measurement across a broad range of temperatures. Different combinations of measurement samples and electrodes can accommodate plates, liquids, gels, and films (sheets) (see Fig. 3). A constant-temperature chamber or thermal shock tester can be used to test dielectric constant and dielectric loss tangent temperature characteristics (see Fig. 4).
In addition, KEYCOM provides automatic measurement systems.
Supported standards include ASTM D-150, JIS C2101, JIS C2141, JIS C 6481, JIS K6911, and JIS C 2111 28.1.2 (method B). Other standards can be supported as well; please contact the company with your specific needs.
Information
Capacitive electrodes for measuring dielectric constant and dielectric loss tangent make possible tan δ measurement across a broad range of temperatures. For details, please contact KEYCOM Corporation.

