Inspection in Assembly of Li-ion Battery Packs for EVs
Introduction to the assembly of battery packs and their inspection.
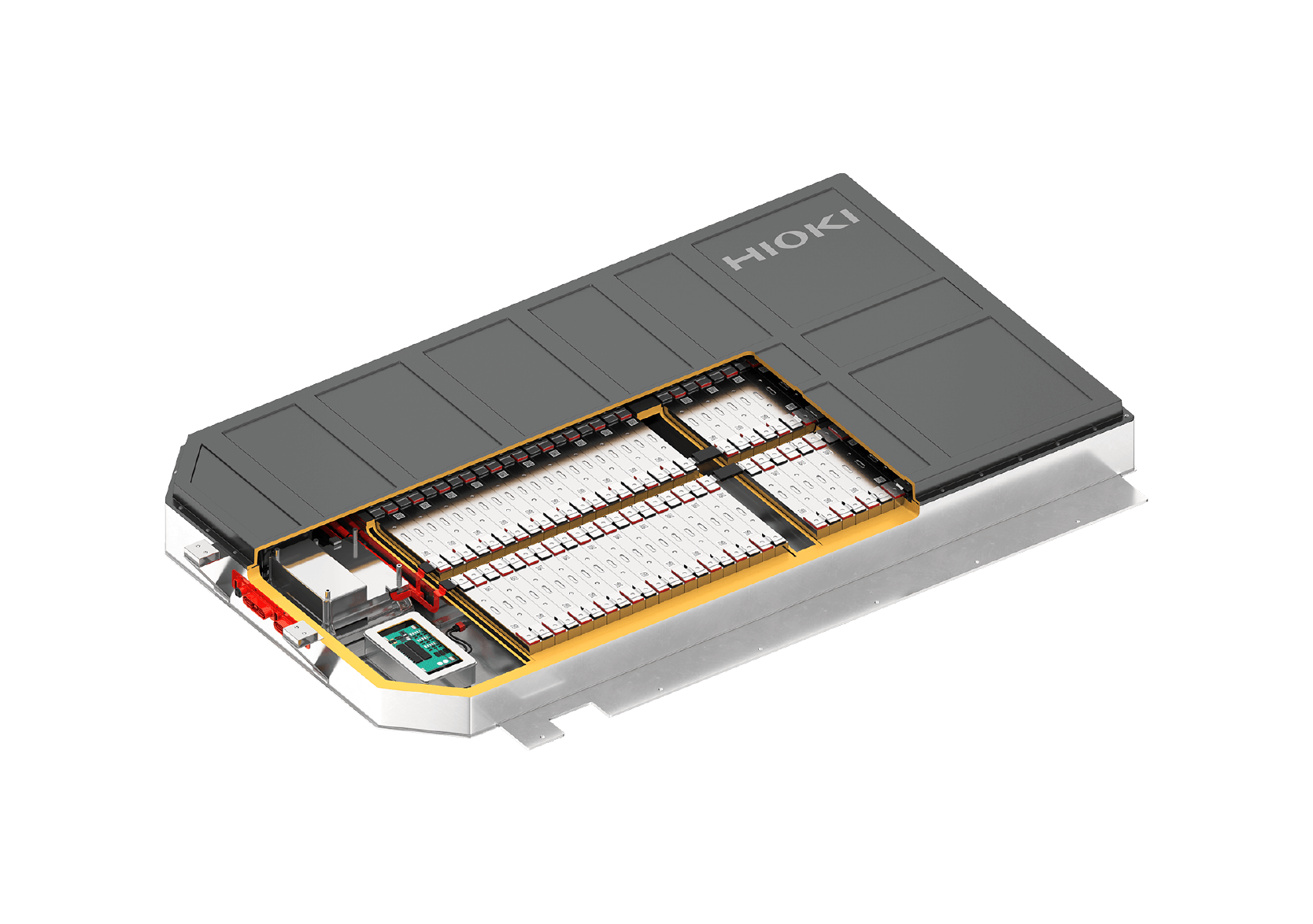
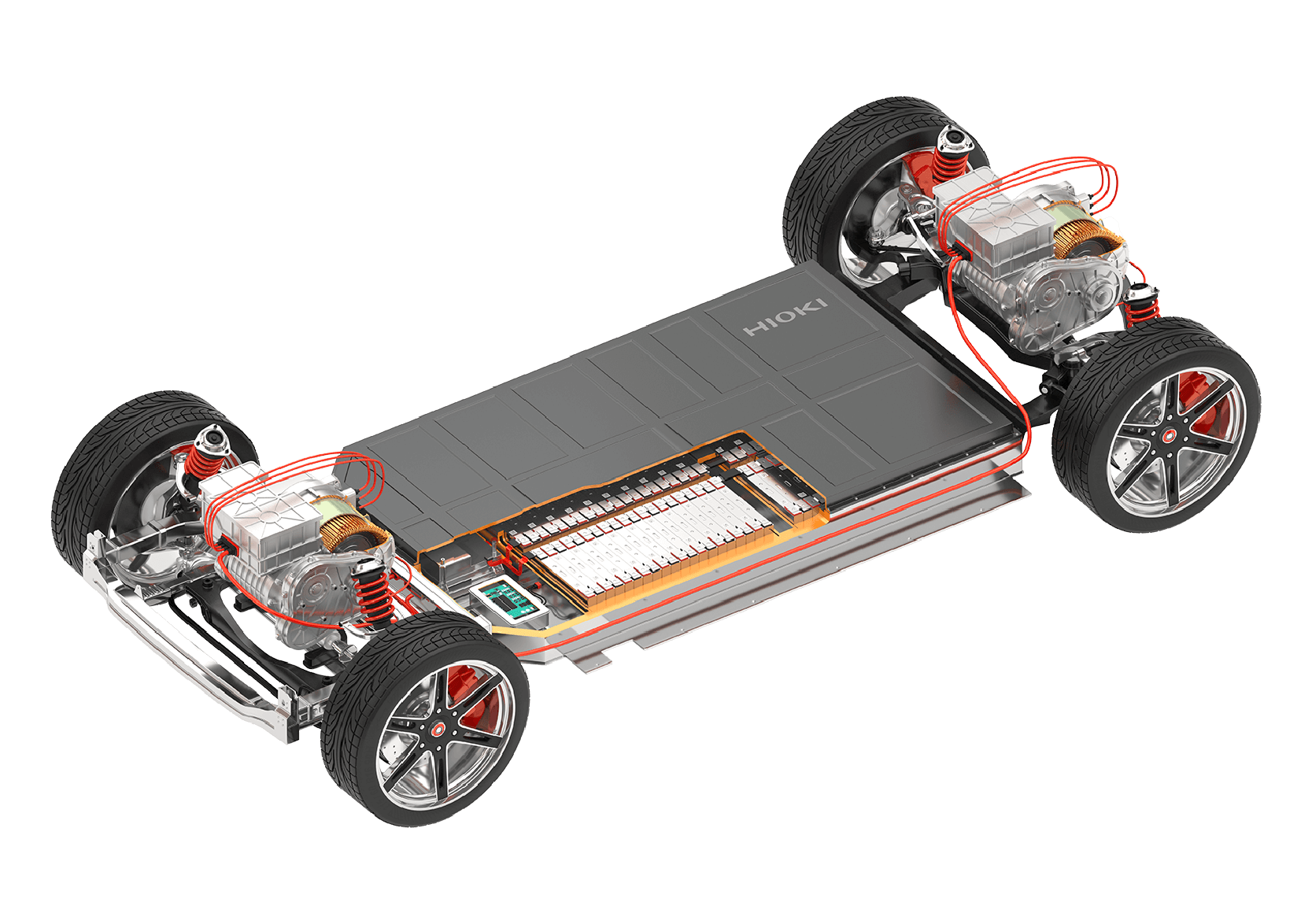
Assembly process of Li-ion battery packs for EVs
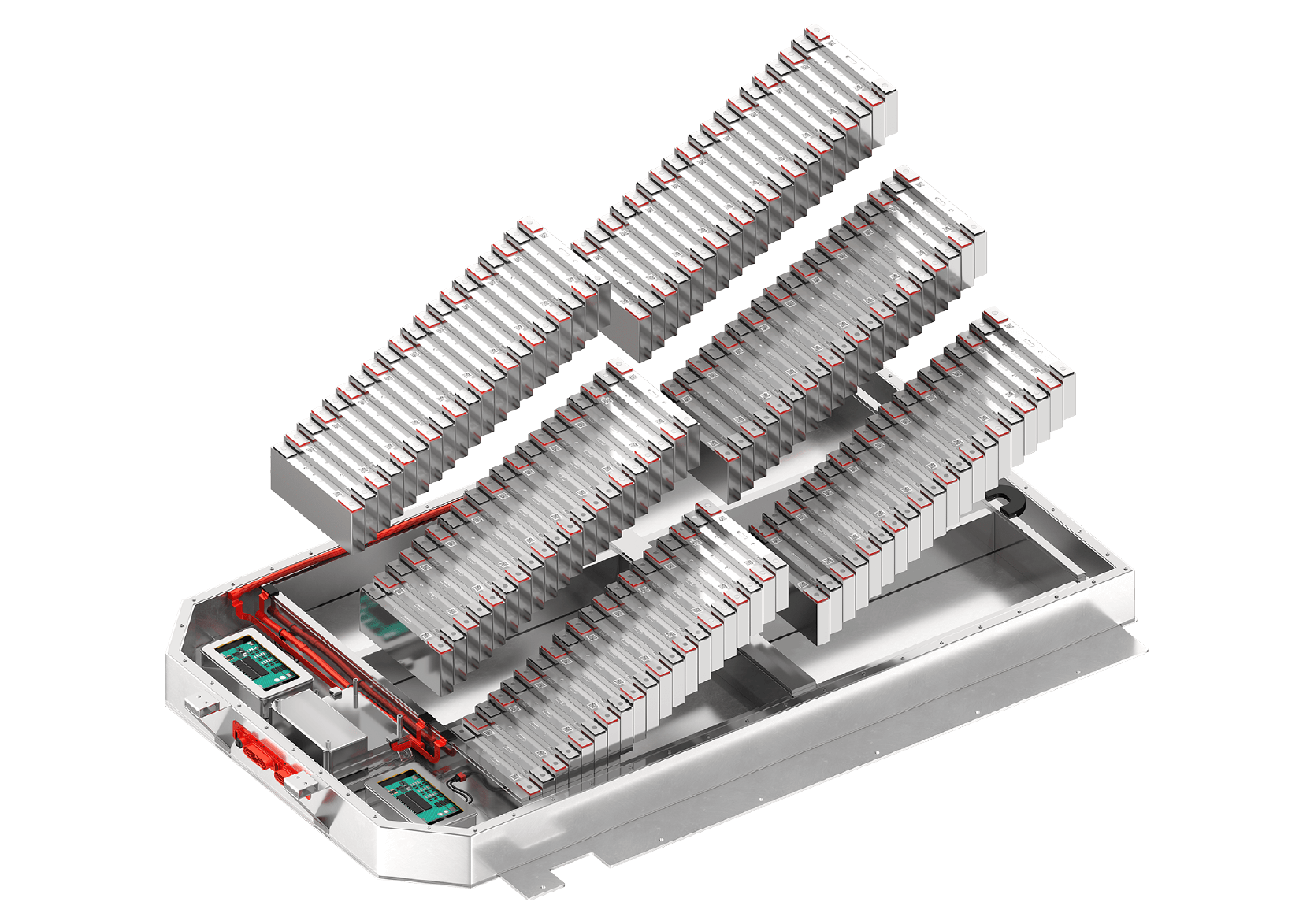
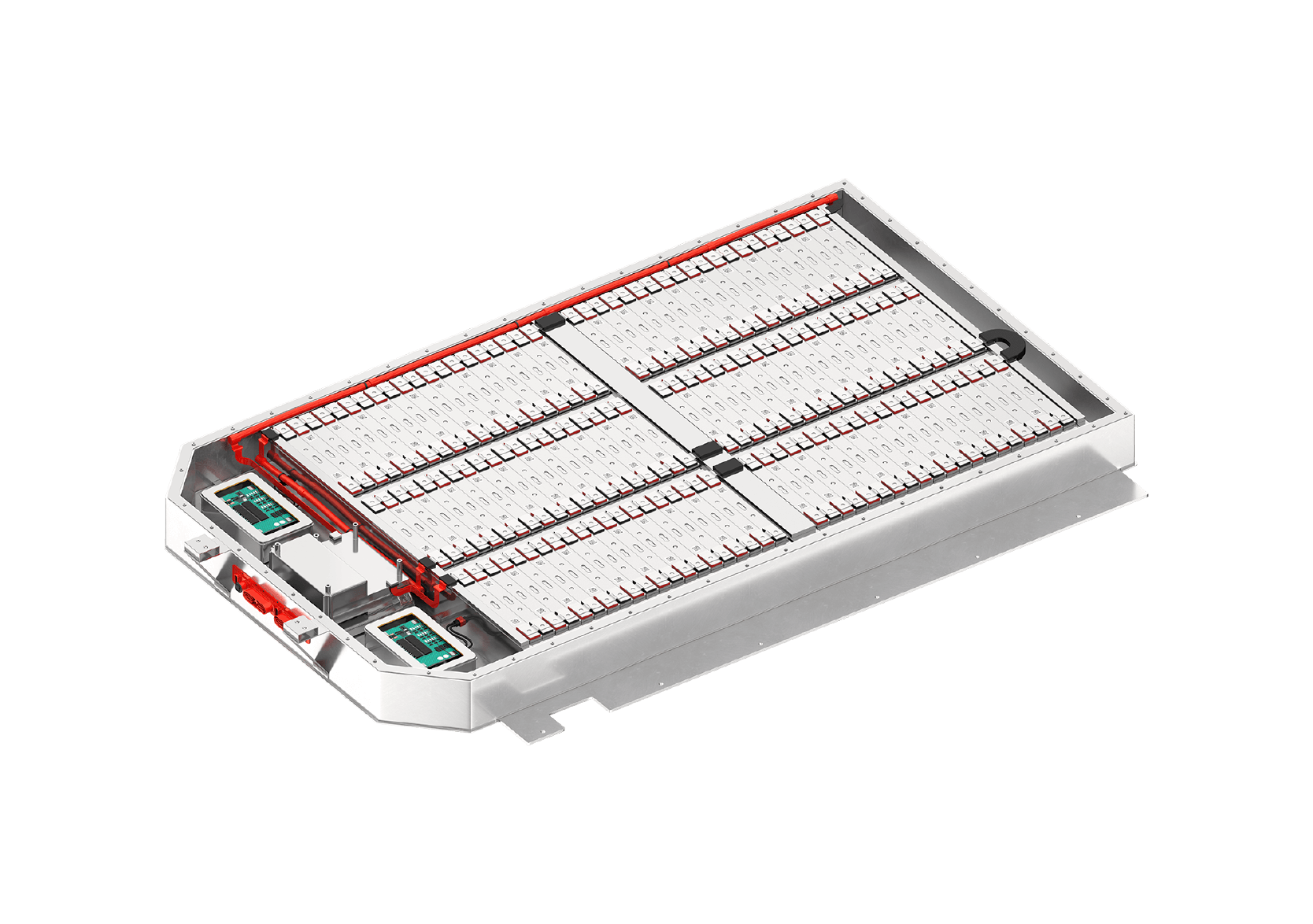
Assembly from cell batteries to pack batteries
The smallest unit of a battery is called a cell. The three common shapes of cells are cylindrical, prismatic, and pouch. The state in which the cells are connected is called a module, and the state in which the modules are connected is called a pack. There are also packs without modules, such as "Cell to Pack".
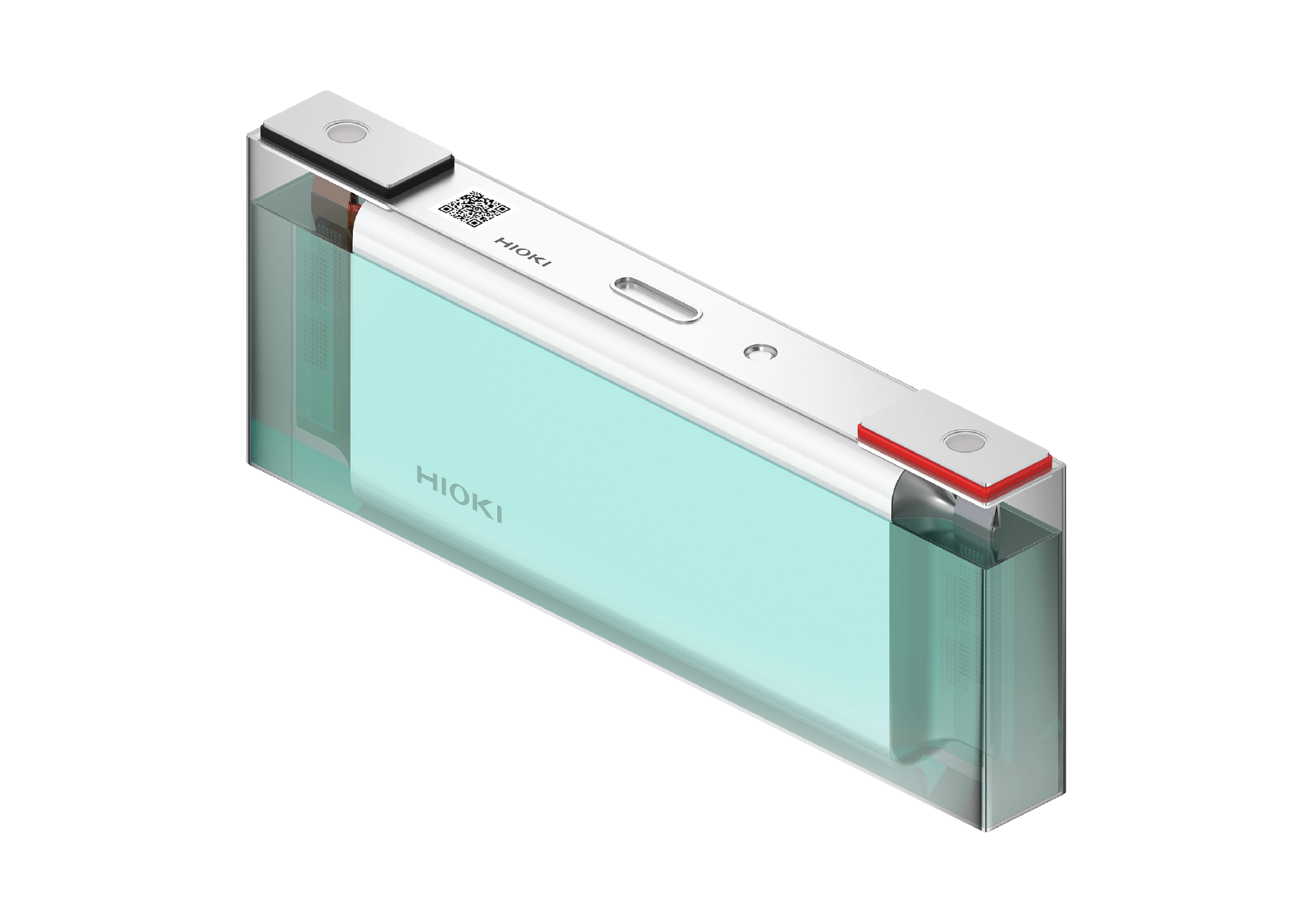
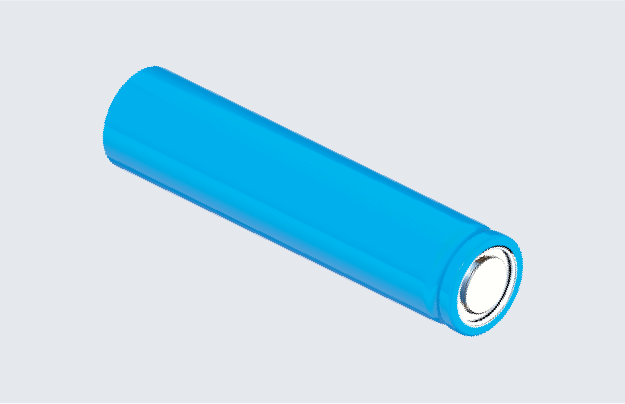 Cylindrical cell
Cylindrical cell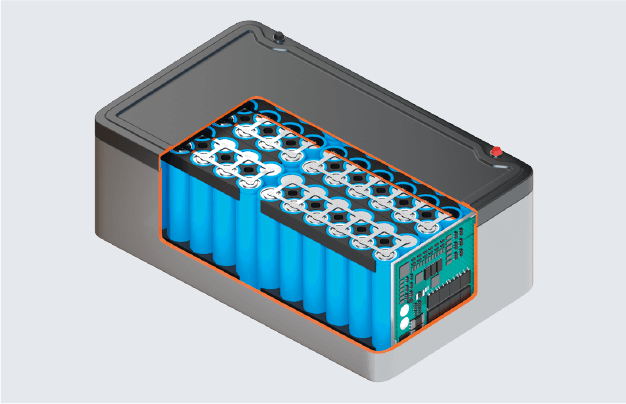 Module with cylindrical cells
Module with cylindrical cells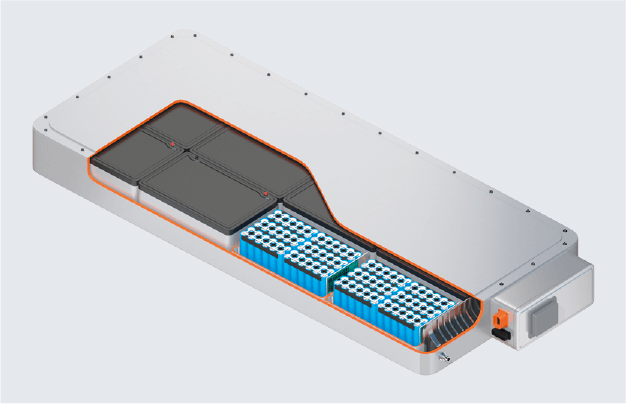 Pack with cylindrical cells
Pack with cylindrical cells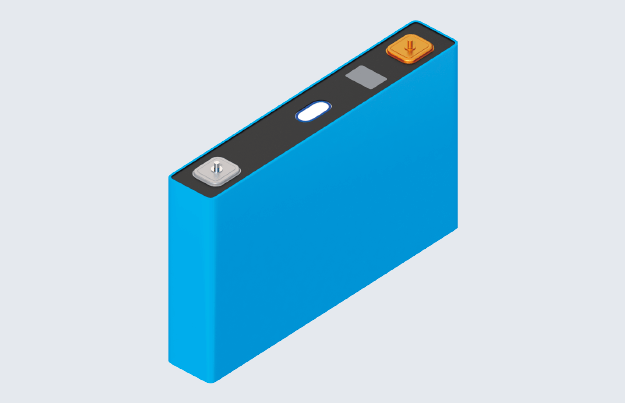 Prismatic cell
Prismatic cell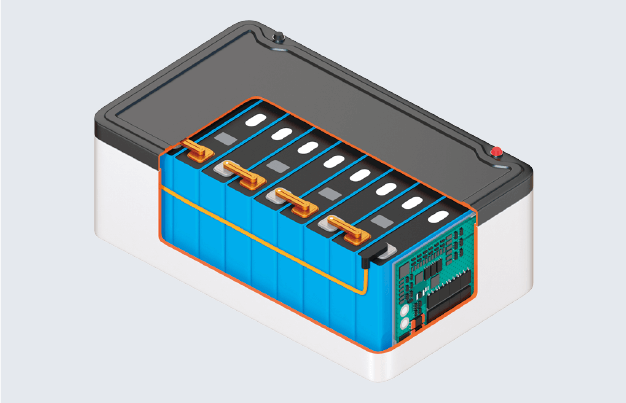 Module with prismatic cells
Module with prismatic cells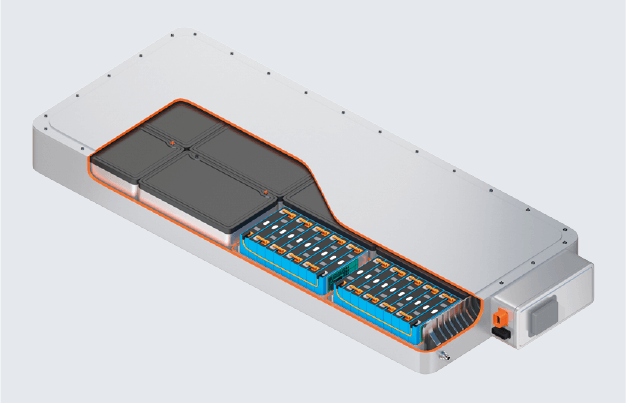 Pack with prismatic cells
Pack with prismatic cells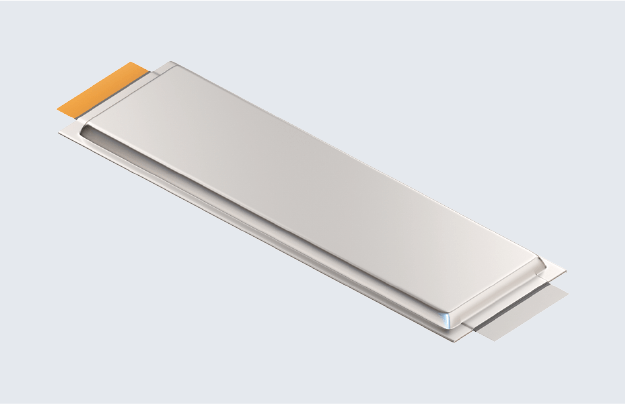 Pouch cell
Pouch cell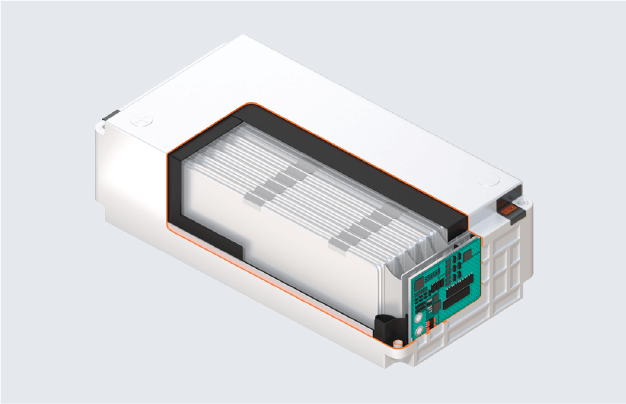 Module with pouch cells
Module with pouch cells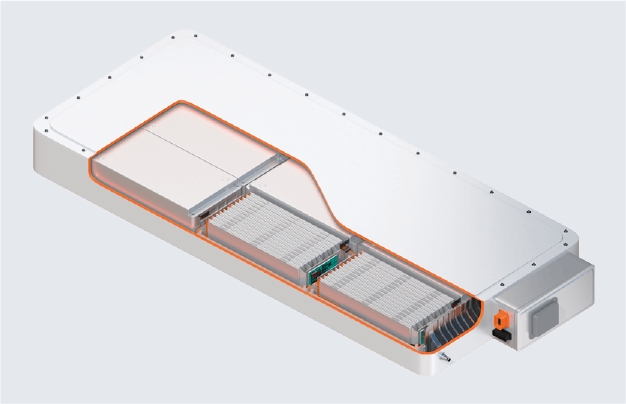 Pack with pouch cells
Pack with pouch cells
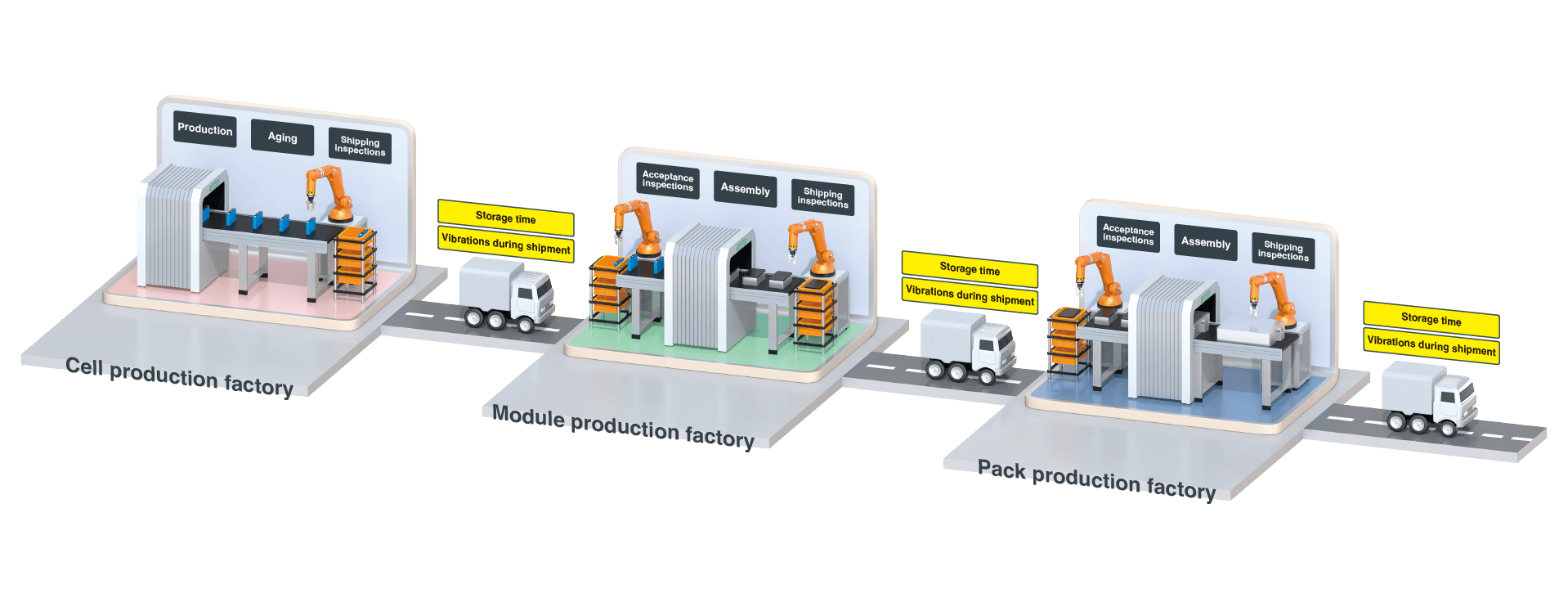
Cells produced at the cell production factory are shipped to the module production factory after undergoing a shipping inspection. Batteries go through an acceptance inspection before they are put together into modules and packs. This is because things like vibrations during shipping and even the passing of time can cause batteries to defect.
Li-ion battery pack inspection methods
Insulation resistance testing
It is necessary to keep the electrodes and enclosure (case), insulated from each other. Failure to keep those components properly insulated — in other words, insufficient insulation resistance — could lead to a risk of ignition or fire accidents.
- BATTERY INSULATION TESTER BT5525

- INSULATION TESTER ST5520

- SUPER MEGOHM METER SM7110

- SUPER MEGOHM METER SM7120

The above instruments measure the insulation resistance between the electrode and the enclosure.
 BT5525
BT5525
Dielectric withstand testing (Hi-Pot testing)
Battery packs must have sufficient dielectric strength for the application. Insufficient dielectric strength may result in electric shock or other accidents.
The above measuring instruments inspect dielectric strength by applying a voltage for a set amount of time.
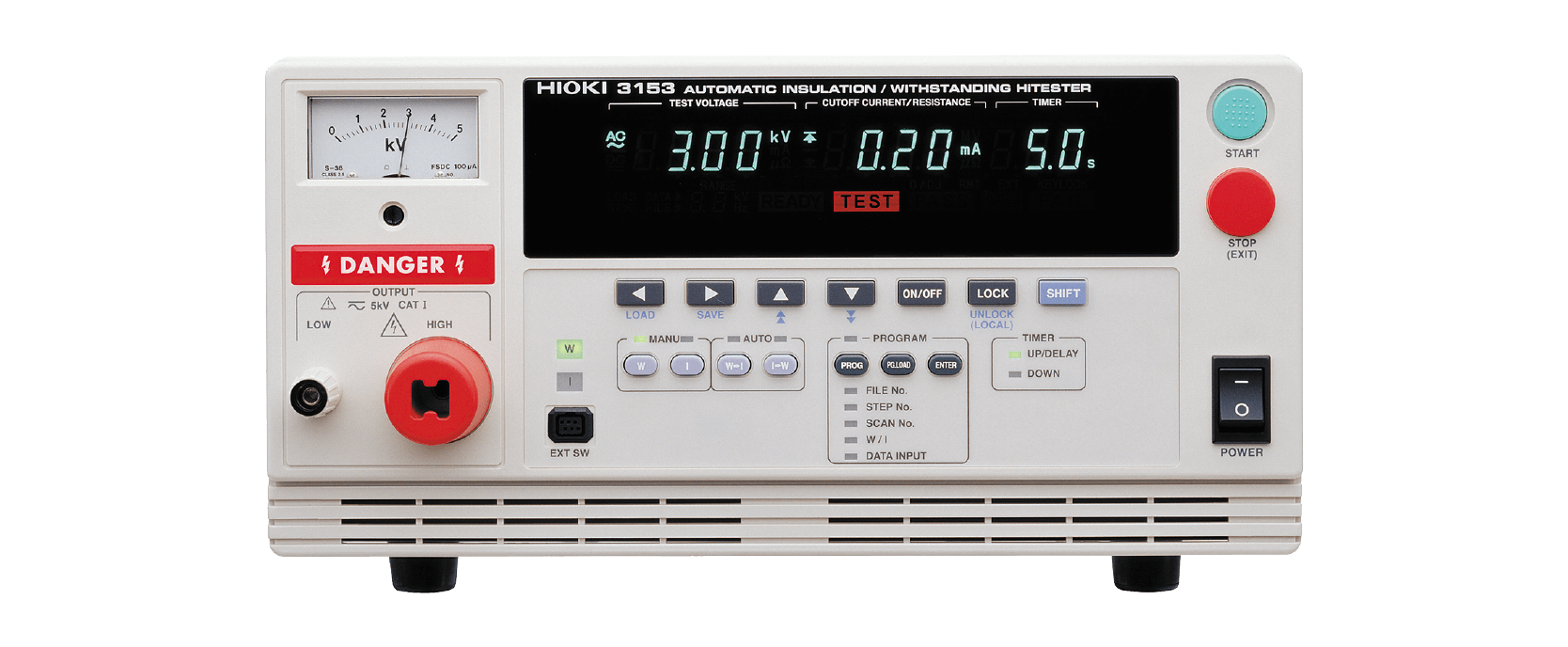 3153
3153
Difference between insulation resistance testing and withstand voltage testing
Insulation resistance tests are used to detect insulation flaws by measuring resistance values. Hi-Pot testing determines whether dielectric breakdown occurs.
Internal resistance testing
Batteries with high internal resistance tend to generate more heat and degrade faster. When batteries degrade, their capacity declines, and their internal resistance rises. Internal resistance also changes over time or as a consequence of vibrations during shipment. It’s essential to eliminate cells with high internal resistance by carrying out an inspection each time cells are shipped or received.
Open-circuit voltage (OCV) testing
A battery’s voltage is known as the open-circuit voltage (OCV) when it is not connected to any load. OCV values gradually decline due to self-discharge, a characteristic of batteries. When a battery has an internal defect, self-discharge increases, causing the OCV to increase beyond the defined value.
The above instruments simultaneously measure the "internal resistance" and "OCV" of batteries. The BT3564A or BT3564 is best suited for measuring the OCV of high-voltage packed batteries.
The DM7275 and DM7276 measure "OCV" and display measurements to 7 1/2 digits, allowing the user to more accurately confirm changes in OCV.
 BT3562A
BT3562A
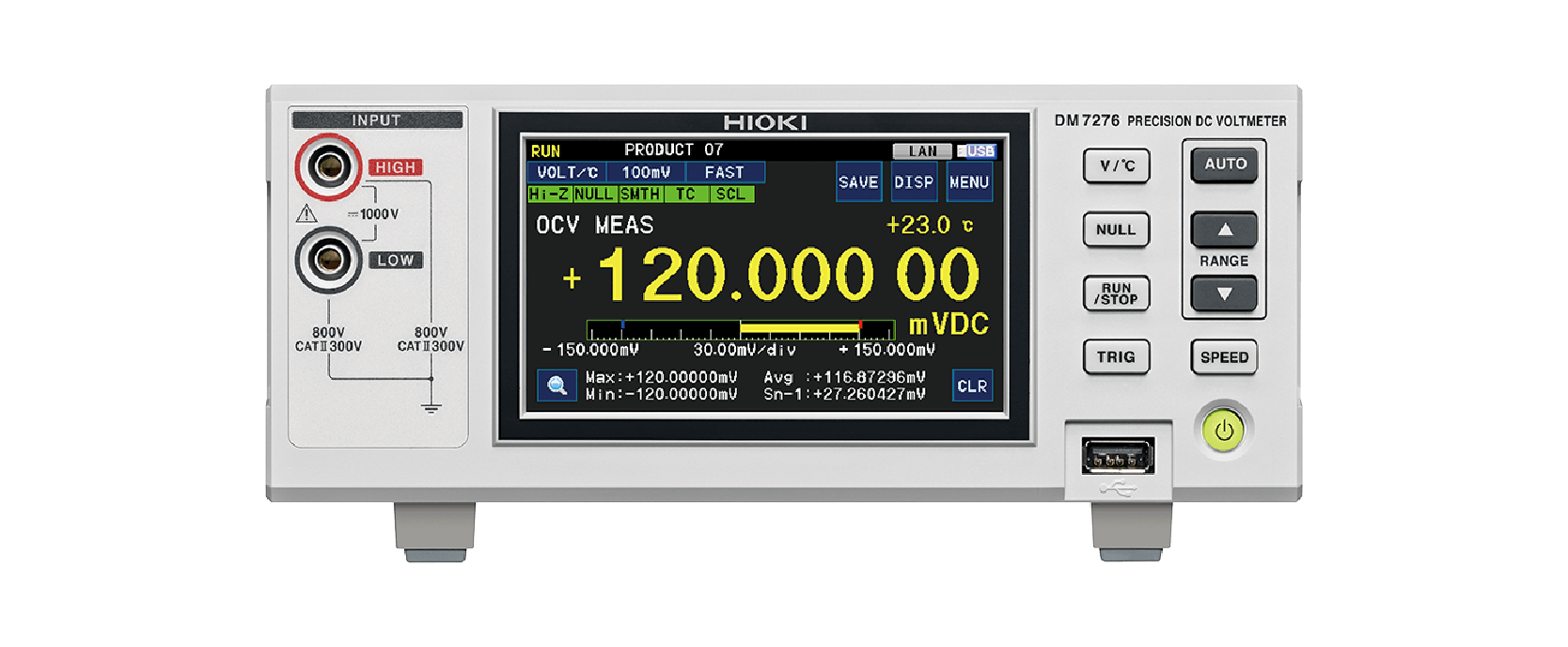 DM7276
DM7276
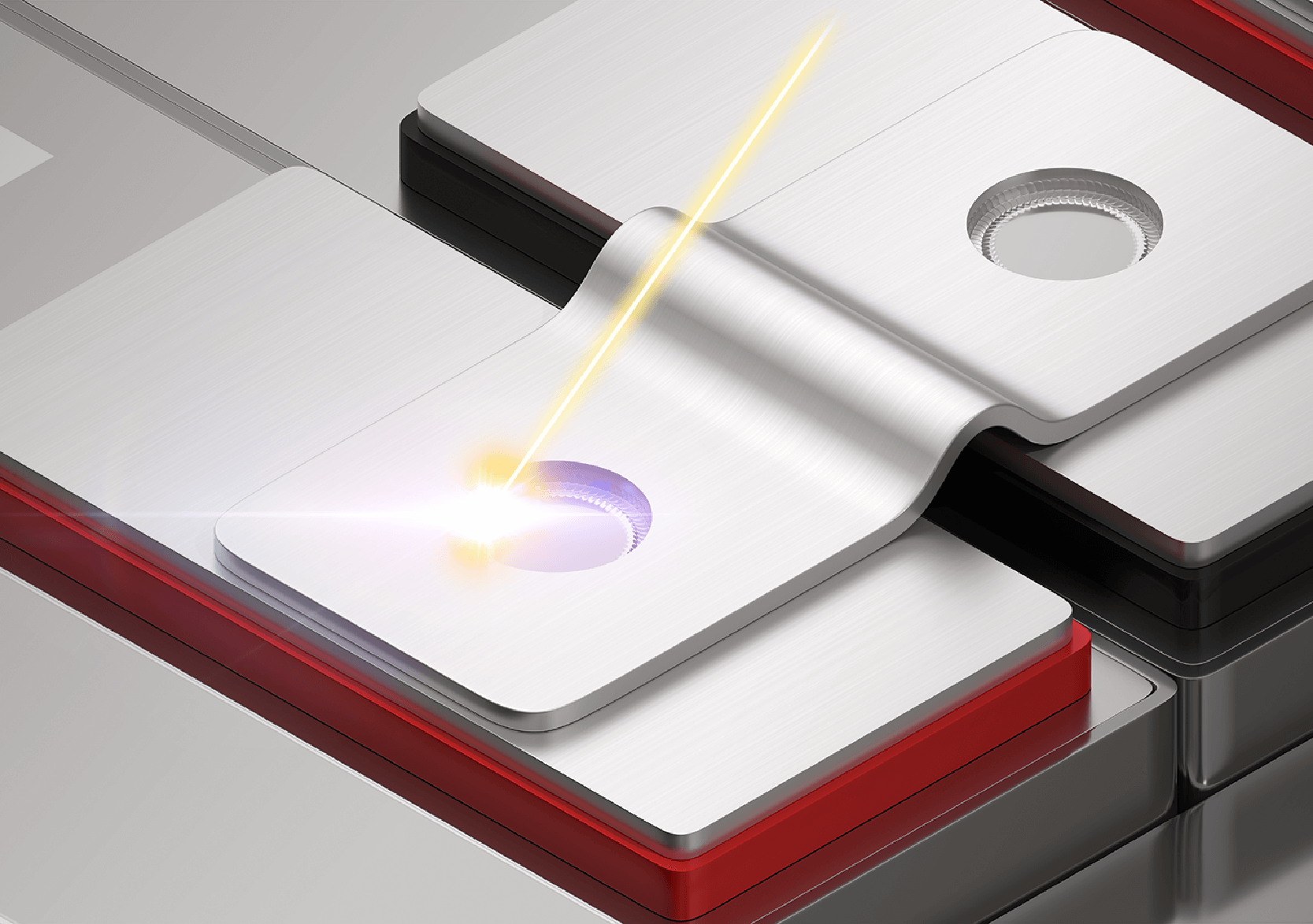
Weld resistance testing
If welds connecting battery components are insufficient, the resistance between components will increase significantly, resulting in electrical energy loss and battery overheating. Such heating can reduce the battery’s service life or cause a fire.
The above instruments measure the resistance between welded components. The RM3546 features protection against over-input up to 60 V.
 RM3546, Z3003
RM3546, Z3003
Reducing testing times with multichannel measurement
Testing times can be reduced by increasing the number of measurement channels, helping shorten lead times.
Using the above device allows you to increase the number of channels for the BT3560 series, RM3546, RM3545A series, and DM7270 series. It also enables simultaneous control of two types of measuring instruments.
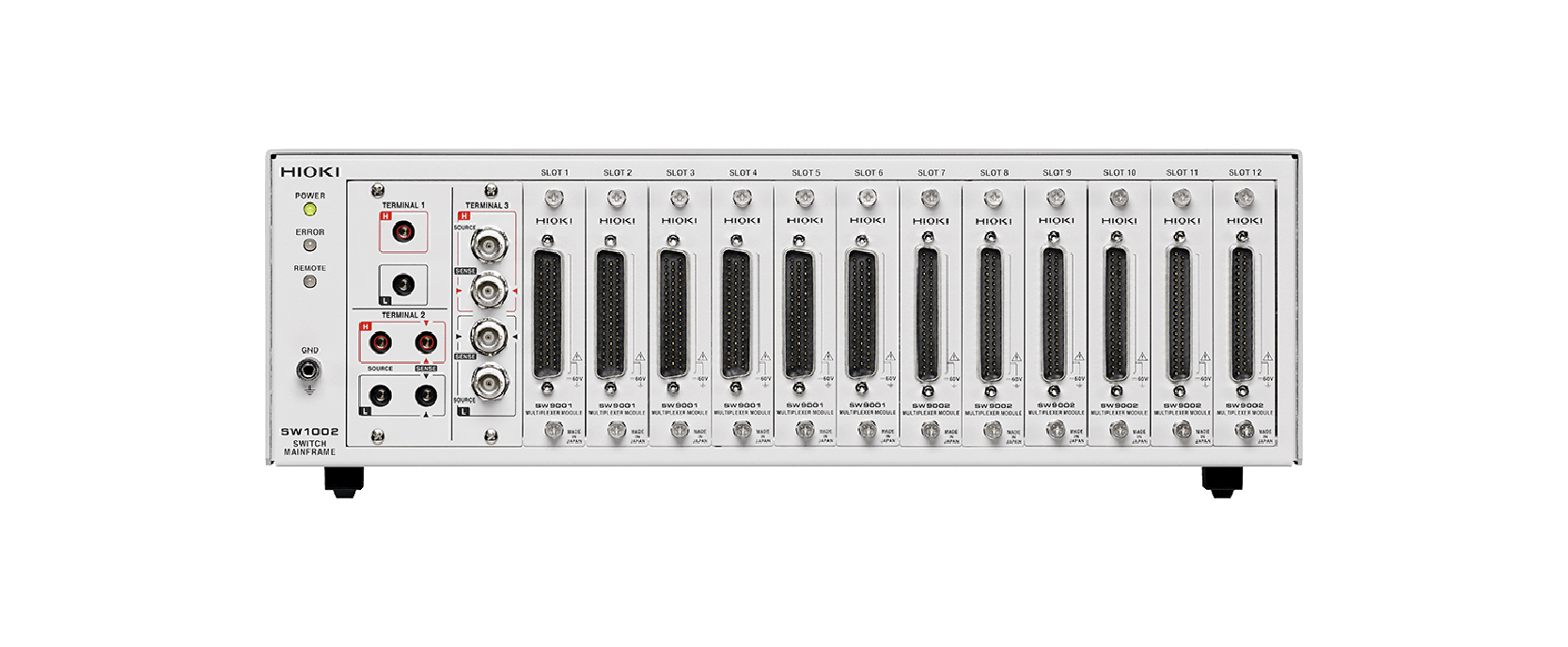 SW1002
SW1002