6 Electrical Tests in the Electric Motor Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process of the motor can be broadly divided into three stages as shown in Fig. 1.
- Rotor assembly
- Stator assembly
- Motor assembly
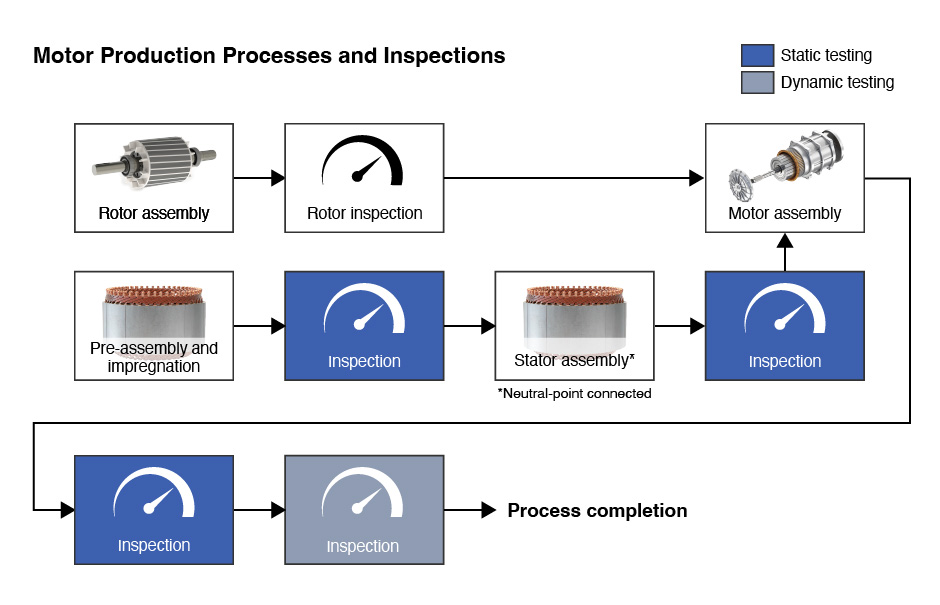 Fig. 1 Motor manufacturing process
Fig. 1 Motor manufacturing process
The motor manufacturing process comprises three primary stages: rotor assembly, stator assembly, and motor assembly. To ensure high-quality motor production, rigorous mechanical and electrical inspections are conducted at each stage. Following assembly, static and/or dynamic evaluations are performed to assess safety and performance. This article will focus on six crucial static electrical tests performed on the stator and finished motor to enhance overall quality.
Six static electrical tests
- 1.Low resistance measurement
- 2.Inductance measurement
- 3.Insulation resistance (IR) measurement
- 4.Hipot test
- 5.Layer short test, also known as surge test
- 6.Partial discharge test
Low resistance measurement
Measuring resistance values helps ensure the quality of motor windings, thermistors, and component connections. For windings, resistance measurements can reveal issues such as incorrect wire thickness, variations in the number of turns, short circuits, disconnections, and welding defects. For thermistors in motors, measuring resistance confirms that the correct parts are properly installed and functioning. A resistance meter is used to evaluate all of these aspects in a reliable way.
| Measurement stage | Locations |
|---|---|
| Inspection of impregnated stators | Windings |
| Inspection of stator assembly | Windings, thermistors, welded parts on the stator |
| Static inspection of finished motors | Windings, thermistors |
Inductance measurement
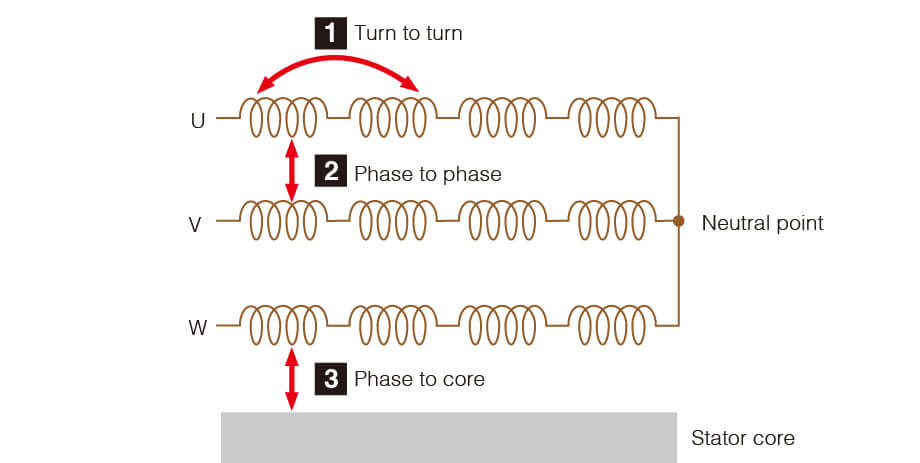
By measuring the winding inductance, it is possible to check the winding balance between the phases. Unbalanced phases will result in uneven motor rotation and cause the motor to lose consistency with the motor driving. Inductance can be measured with an LCR meter.
| Measurement stage | Locations |
|---|---|
| Inspection of impregnated stators | Windings |
Insulation resistance (IR) measurement
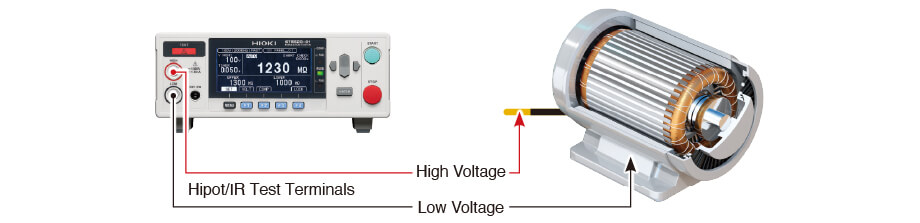
The insulation resistance (IR) measurement is done to find faulty products that have insulation resistance values lower than a standard set by the technician. This helps avoid electric shocks and short-circuit issues. To measure insulation resistance, you can use a tool like an insulation resistance meter or a hipot tester with an IR measurement function. The probing location for this test may vary depending on the specific process.
| Measurement stage | Locations |
|---|---|
| Inspection of impregnated stators | Between windings |
| Inspection of stator assembly | Between windings and core |
| Static inspection of finished motors | Between stator and housing |
Hipot test
The hipot test is conducted to identify defective insulation products that do not have sufficient dielectric strength against the motor's rated voltage. This test is performed to assess the insulation resistance between the coil and the housing (core) that people may come into contact with. Typically, the hipot test is conducted at a higher test voltage than the insulation resistance measurement. The equipment used in this test detects insulation breakdown by applying AC or DC voltage and measuring leakage current. A hipot tester is commonly used for conducting this test.
| Measurement stage | Locations |
|---|---|
| Inspection of impregnated stators |
|
| Inspection of stator assembly | Between the stator and other parts |
| Static inspection of finished motors | Between stator and housing |
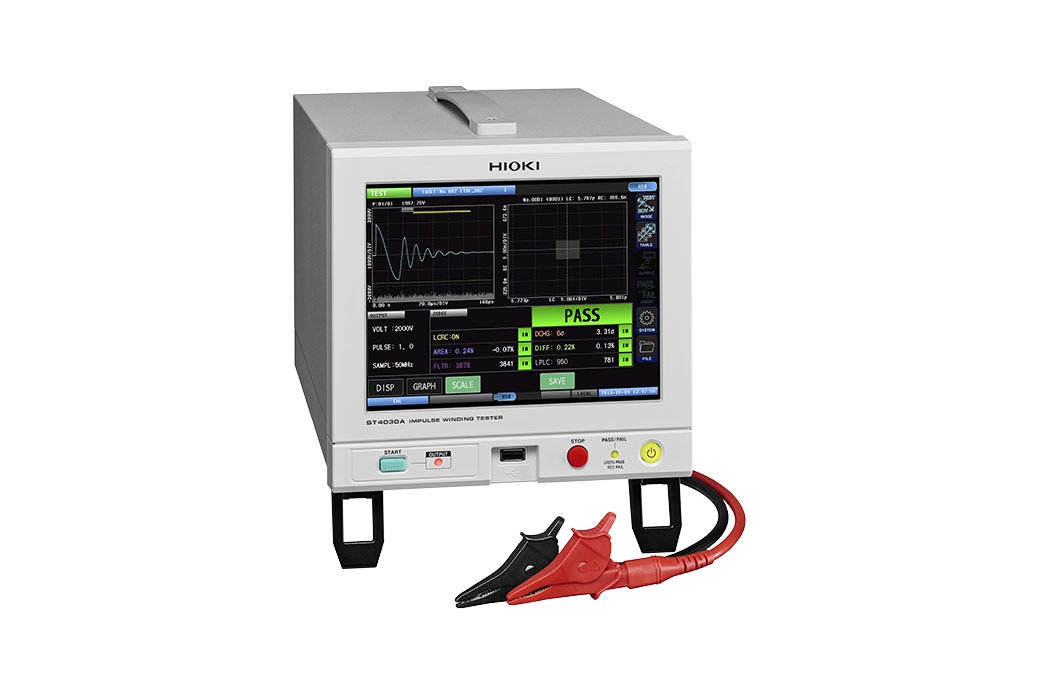
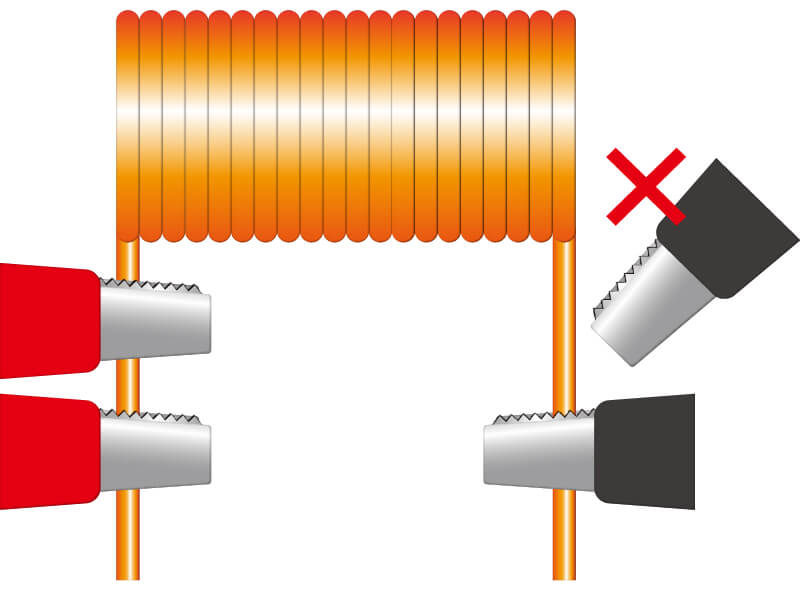
Layer short test
The layer short test is also referred to as the surge test. By applying an impulse/surge (high voltage), we inspect whether the coil winding's coating is properly insulating. It detects layer shorts (1-turn shorts) that are difficult to find with resistance and inductance measurements. The layer short test can be conducted by using an impulse winding tester (surge tester).
| Measurement stage | Locations |
|---|---|
| Inspection of impregnated stators | Between windings of the same phase |
| Inspection of stator assembly | Between windings of the same phase |
Partial discharge test
Partial discharge (PD) testing helps catch small or partial discharges before they become major issues, pinpointing possible problems that the hipot test might miss. Partial discharges damage the coil's wires. This damage will cause more partial discharges and eventually normal discharges to occur in the same location. Eventually this leads to complete dielectric breakdown. By finding these partial discharges, you can reduce the risk of motor failure due to insulation breakdown. There are two types of partial discharge tests: AC PD test, conducted with AC high voltage sources, and surge PD test (also known as "impulse PD test"), performed using a surge generator. Each test detects insulation issues in different areas of motors, so it is crucial to perform both. A partial discharge detector is used to conduct partial discharge tests. Additionally, a hipot tester is required as an AC high voltage source, and an impulse winding tester is needed as an impulse/surge power source.
| Measurement stage | Locations |
|---|---|
| Inspection of impregnated stators | AC PD tests: [2] Phase-to-phase and [3] phase-to-ground/stator core |
| Inspection of stator assembly |
|
| Static inspection of finished motors |
|
Measurement solutions from Hioki
At Hioki, we provide solutions for testing and measurement that correspond to all of the tests above.
| Measurement and test type | Product | Features |
|---|---|---|
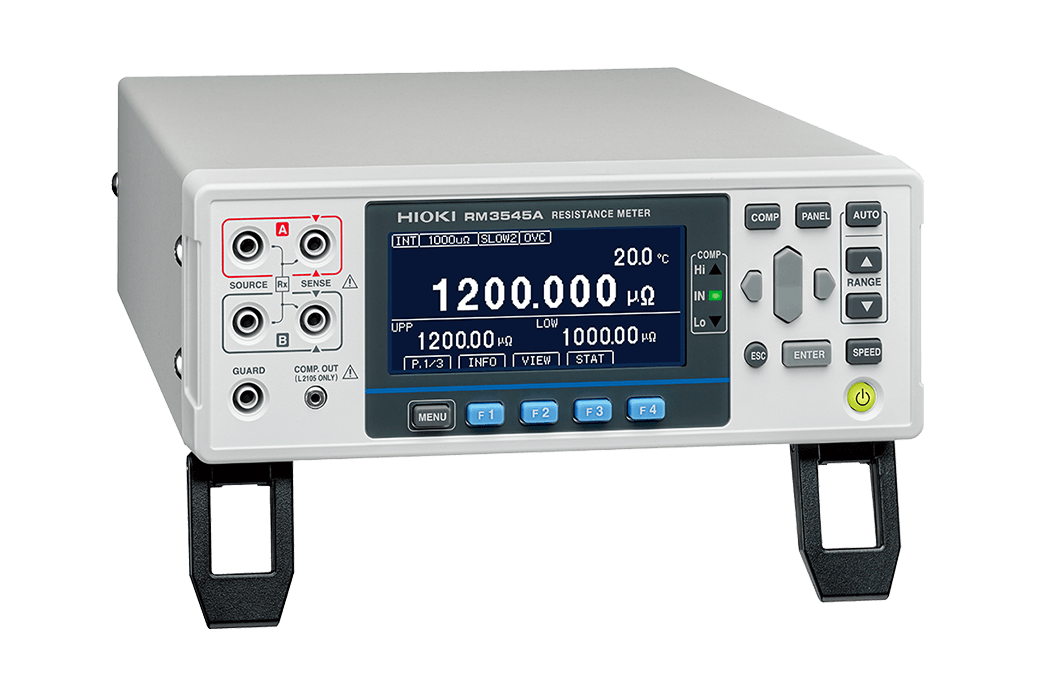
| Low resistance measurement | RM3545A |
|
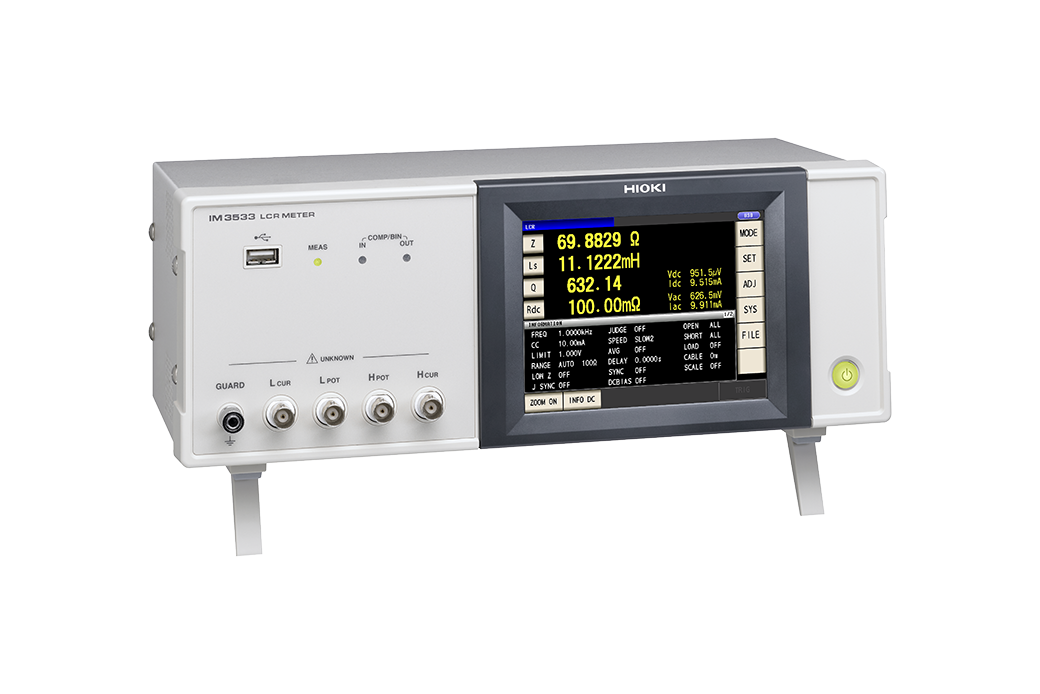
| Inductance measurement | IM3533 |
|
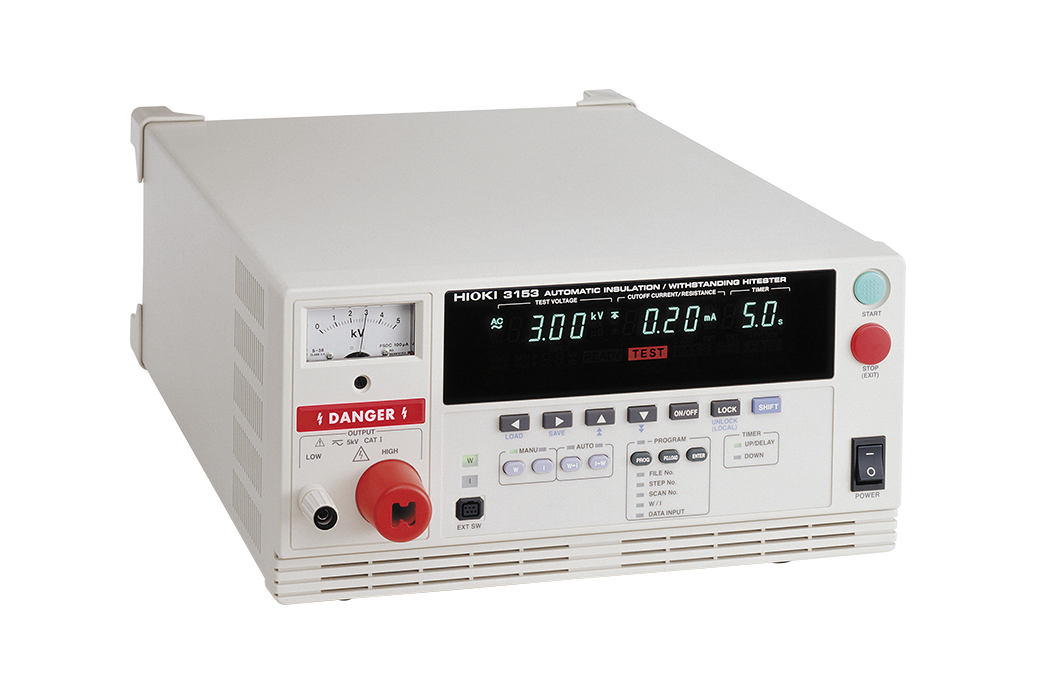
| Insulation resistance measurement | 3153 |
|
| Hipot test | 3153 |
|
| Layer short test | ST4030A |
|
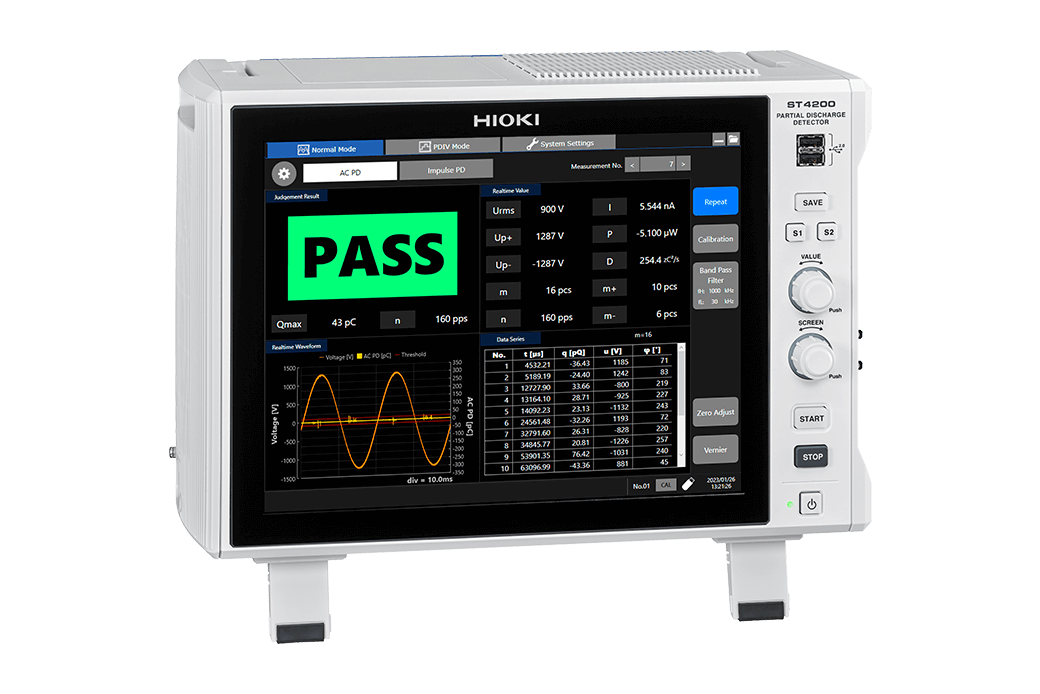
| Partial discharge test | ST4200 |
|
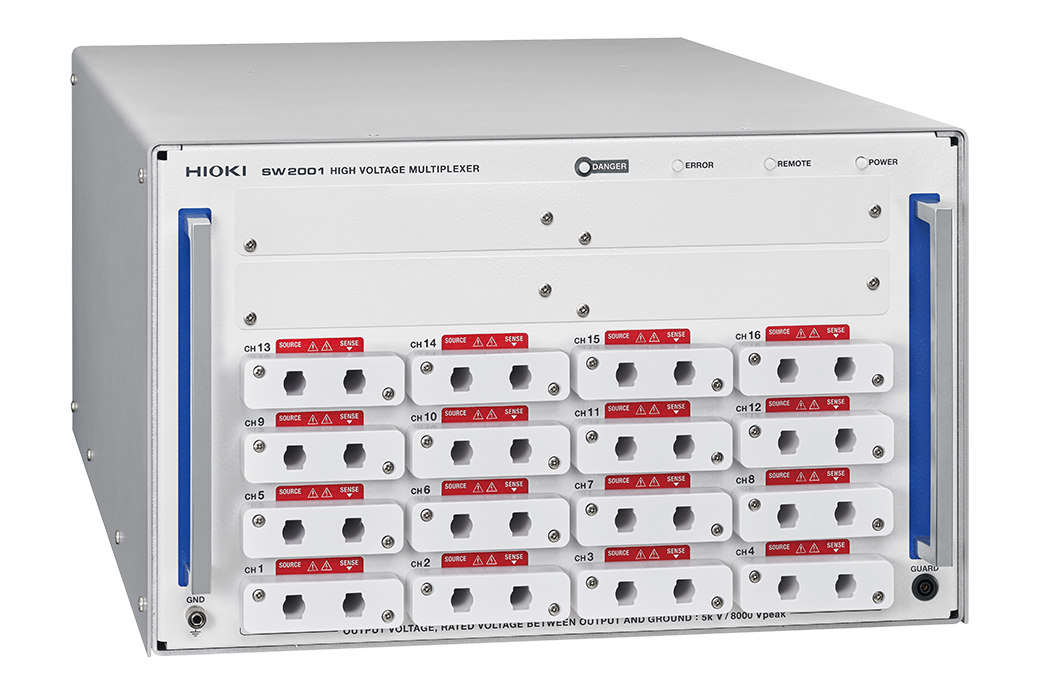
Additionally, Hioki also offers the dedicated multiplexer SW2001, which can integrate all of these electrical inspections and measurement of stators and finished motor products.
The SW2001 is a multiplexer with a stunning high and low voltage capability. It can accommodate not only high-voltage tests, such as insulation resistance measurement, hipot testing, and impulse winding testing, but also 4-terminal low-voltage measurement, such as winding resistance measurement and inductance measurement.
Downtime and disruptions in production can be significantly reduced by effectively addressing issues such as circuit failures and measurement inaccuracies arising from high voltage testing. The SW2001 is highly durable and has guaranteed measurement performance. This durability translates into decreased maintenance-related time and costs, thus contributing to an overall enhancement in system reliability.
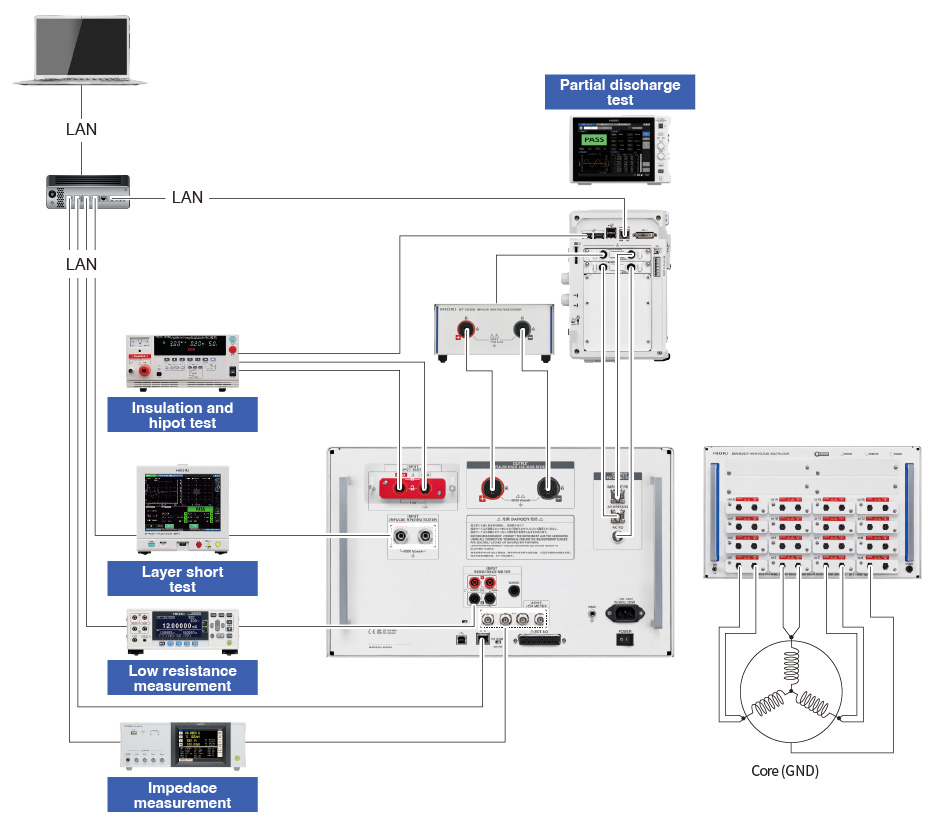 Fig.2 Multiplexer system integrates electrical inspections
Fig.2 Multiplexer system integrates electrical inspections
Conclusion
In order to improve the quality of motors, it is necessary to conduct electrical tests at early stages and solve many issues. At Hioki, we offer a wide range of solutions to address production challenges. If you have any concerns about motor measurement, please do not hesitate to consult with Hioki.