The Reasons for Voltage Increases in Solar PV Systems and Anticipated Overvoltage
To realize a sustainable society, power generation systems that utilize renewable energy are gaining popularity. Due to its low cost and simple installation, photovoltaic power generation is becoming increasingly popular.
Reasons why solar photovoltaic (PV) system is becoming high-voltage
Reducing energy loss during power transmission
Power generation efficiency can be improved by switching from a 1000 V system to a 1500 V system. When the current is high, energy loss during power transmission is high. Increasing the voltage and decreasing the current will reduce energy loss. Therefore, the PV systems are being upgraded to higher voltages in order to minimize losses and maximize the utilization of the electrical energy generated.
Cost
A 1500 V PV system requires less cost than a 1000 V system. Since the number of strings in a 1500 V system is approximately 75% less compared to a 1000 V system, the number of combiner boxes, inverters, and the length of cables can be reduced.
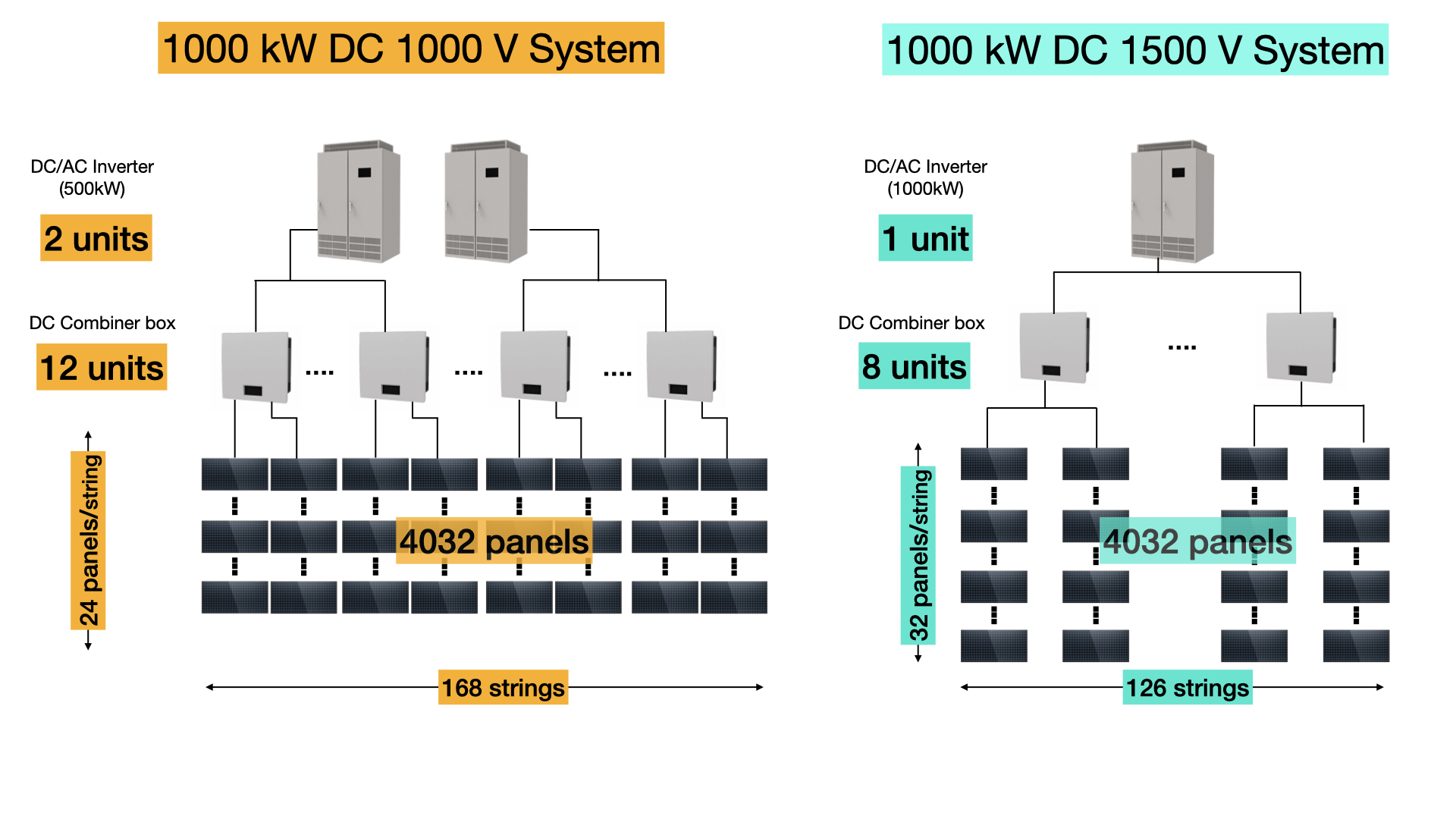
Fig. 1: Examples of 1000 V and 1500 V systems in a 1000 kW photovoltaic power plant
1500 V systems have been rising in popularity as an alternative to the more common 1000 V systems due to their lower cost.
Category classification of solar PV modules
Because PV system facilities are becoming increasingly high voltage, as are transient overvoltages, the dangers associated with maintenance operations are growing. The safety standard EN 61010 series classifies measurements into CAT II, CAT III, and CAT IV according to the measurement location. The category is determined based on the voltage to ground rating, current capacity, and transient overvoltages that occur at the point of measurement. Fig. 2 and Table 1 show the measurement locations and measurement categories.
In addition, according to the standard for Photovoltaic (PV) module safety qualification (IEC 61730-1), PV modules are treated as overvoltage category III. Therefore, for measurement purposes, an instrument categorized as measurement category III is required.
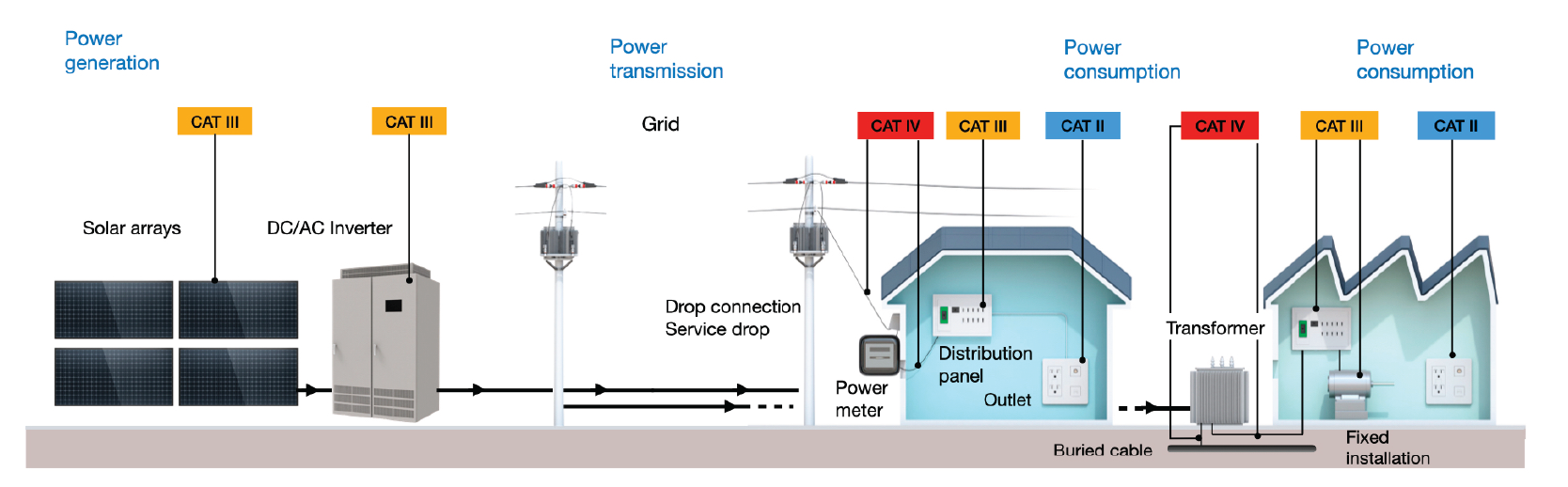
Fig. 2: Measurement Locations and Measurement Categories
| Measurement category | Description |
|---|---|
| CAT II | From the power plugs of devices that are connected to power outlets to the devices' power supply circuits |
| CAT III | Power wiring and power supply circuits of devices that are connected directly to a distribution panel (for example, permanently installed equipment) and wiring from distribution panels to wiring terminals on the back side of power outlets. |
| CAT IV | Buildings' electric service drops and circuits connecting service drops to power meters and distribution panels |
Anticipated transient overvoltage
Power lines in factories and similar facilities can have transient overvoltage (impulse voltage) 10 times the power supply voltage. The transient overvoltage of the measurement points must be predicted in advance, and the instrument will require a safety design to withstand such overvoltage. Table 2 shows the list of the requirements for transient overvoltage according to voltage to ground and measurement category. The transient overvoltage of a 1500 V PV system that is classified as CAT III is 10000 V.
| Rated voltage to ground (V) | Transient overvoltage (V) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CAT II | CAT III | CAT IV | 2500 | 4000 | 6000 |
| 4000 | 6000 | 8000 | |
| 6000 | 8000 | 12000 | |
| 8000 | 10000 | 15000 | |
| 12000 | 15000 | 18000 | |
Solutions from Hioki
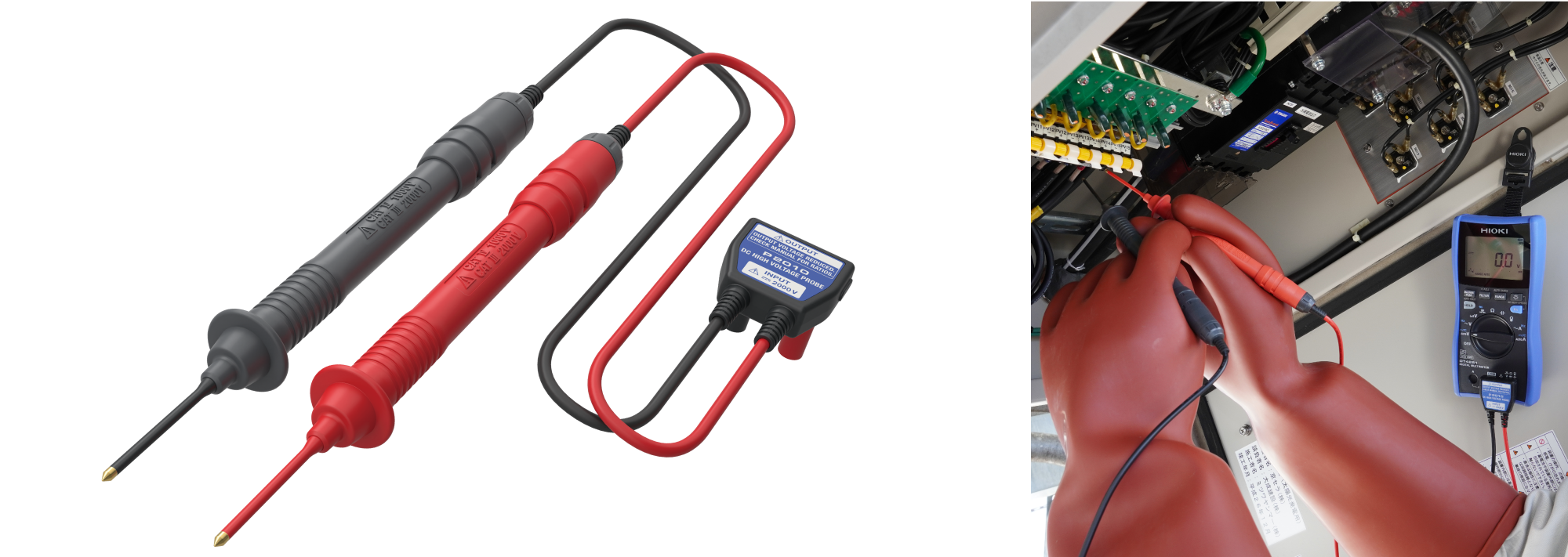
Currently, 1500 V solar installations are becoming increasingly popular, but instruments that can support even higher voltages will be required in the future as larger and more efficient systems become available. In response to the near-term prospect of such applications, Hioki developed the DC High Voltage Probe P2010 to support CAT III 2000 V measurement. This product is designed to safely measure even when there is a transient overvoltage of 15000 V.
Features of P2010
- 1. P2010 can measure high voltages up to CAT III 2000 V simply by connecting to a compatible Hioki clamp meter or digital multimeter.
- 2. The diameter of the tip of the test lead is as small as φ2.6 mm, making probing of the circuit breaker and covered terminals easier.
Introduction of models compatible with P2010
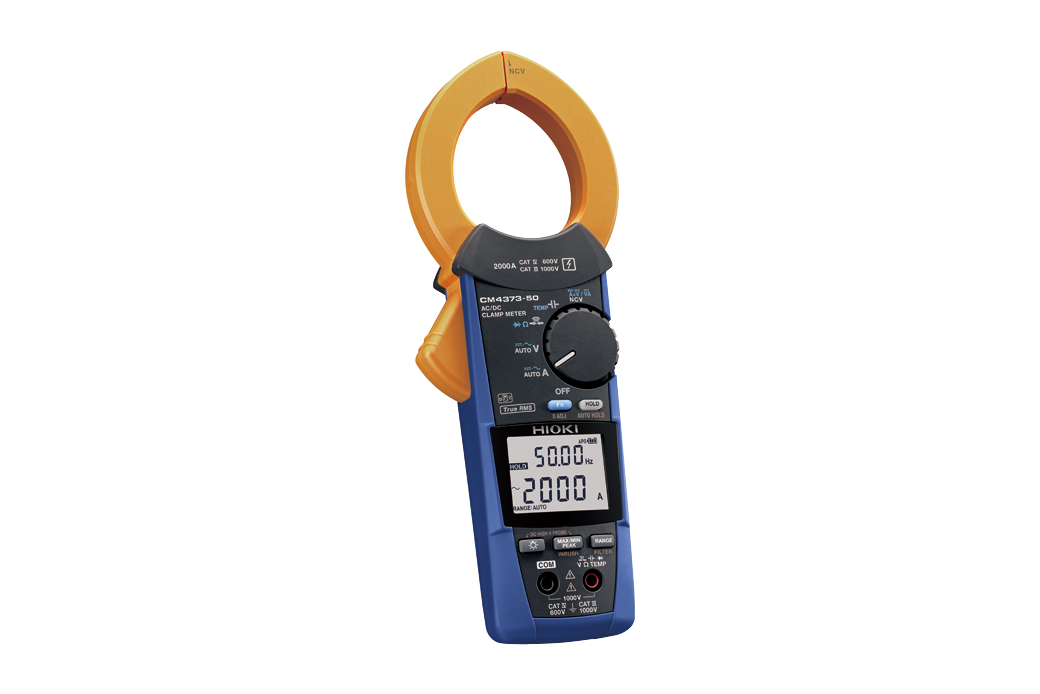
The Hioki clamp meter and digital multimeter that are compatible with the P2010 have a function that allows direct reading of the measured voltage value by converting the voltage reduced by the P2010.- 2000 A AC/DC Clamp Meter CM4373-50
- Two ranges, 600 A and 2000 A, are available to measure a wide range of PV systems, from small-scale photovoltaic installations to mega solar scale systems.
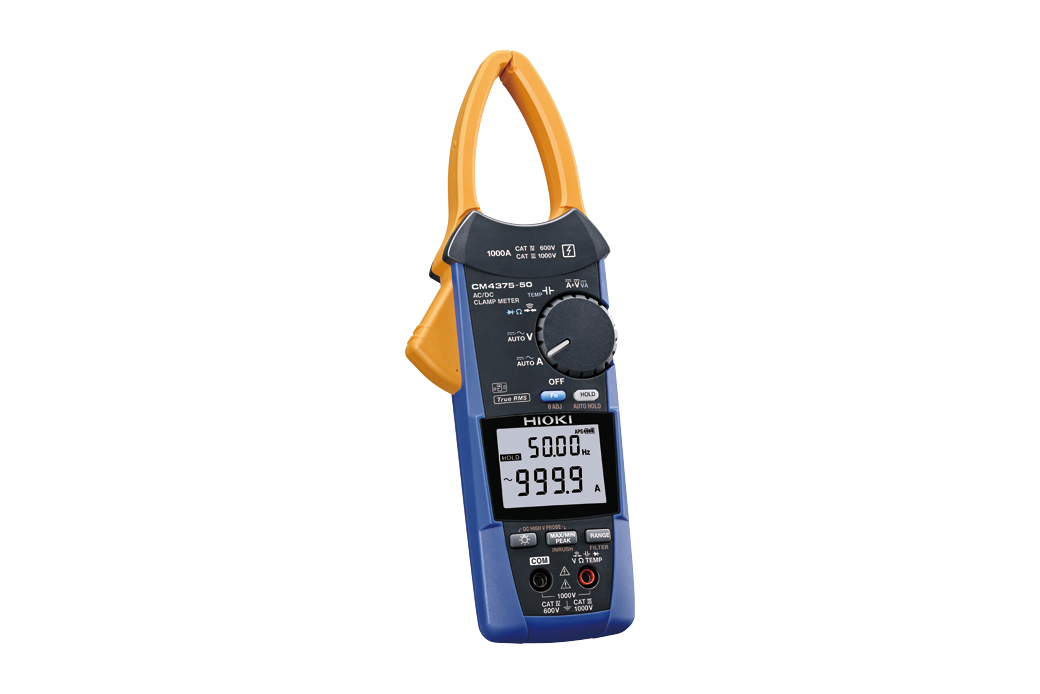
- 1000 A AC/DC Clamp Meter CM4375-50
- With a slim jaw, you can smoothly measure the current in overcrowded and tight spaces.
- The automatic AC/DC detection function lets you measure current and voltage in both AC and DC without switching the ranges. This makes work even more efficient.
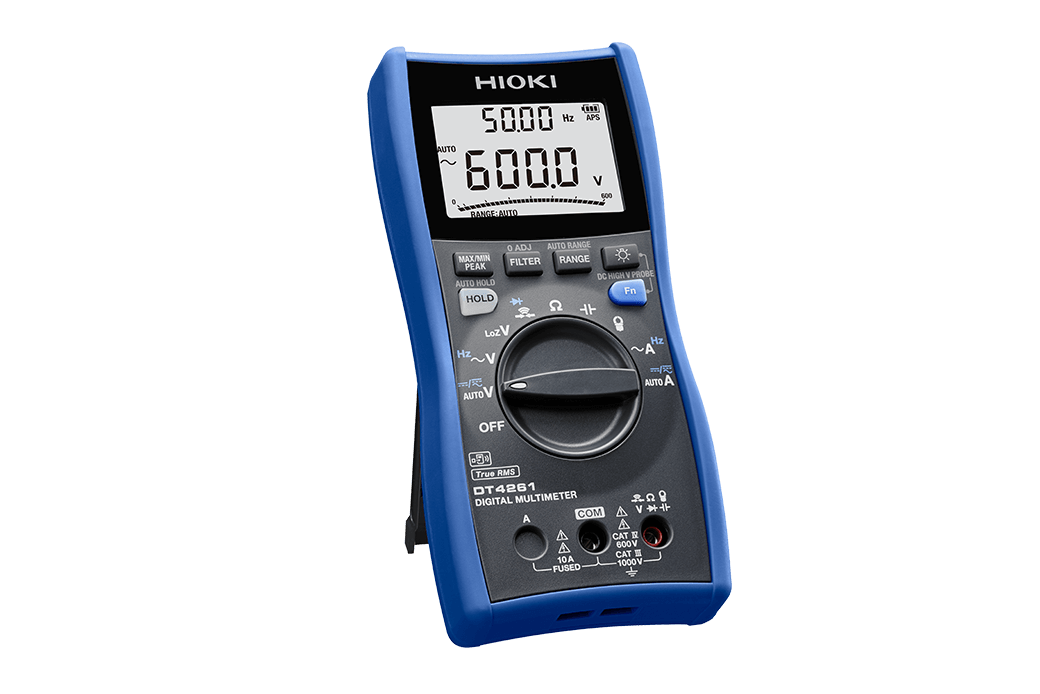
- Digital Multimeter DT4261
- IP 54 rated, waterproof dust-proof which is ideal for outdoor use.
- With the terminal shutter features, this digital multimeter prevents incorrect insertion of test leads and ensures safe and secure measurement.
- Connect your instrument with GENNECT Cross app:
- Making measurements wireless will eliminate transcribing mistakes from paper to PC, save labor, and minimize work hours.
- The comparator function can be used to determine the PASS/FAIL of measured values, which can improve work efficiency.
As larger and even more efficient systems enter into use, the PV system is expected to be higher in the future. Hioki will continue to propose solutions that can be safely and efficiently measured.





