What can a Data Logger do? - The Complete Guide
A data logger is a device that collects and records data over some time. This article delves into data logging, exploring its definition, purpose, and essential features.
Data Logging Defined
Data logging is the systematic process of recording and storing data over time, typically from sensors or instruments, for subsequent analysis and interpretation. This practice involves capturing various parameters, such as temperature, pressure, voltage, or any measurable quantity, and saving it in a digital format. Its primary objective is to provide a comprehensive historical record of data, enabling researchers, engineers, and scientists to make informed decisions and gain valuable insights into various processes and systems.
What Is a Data Logger Used For?
Data loggers are indispensable tools for data acquisition, serving as a crucial component in measurement and monitoring. They are employed across various industries and applications, including scientific research, environmental monitoring, quality control, and industrial automation. These versatile devices collect data from sensors or instruments, convert it into a digital format, and store it for later analysis.
How Do You Choose a Data Logger?
When choosing a data logger for your specific application, it's essential to consider various factors to ensure that it meets your requirements effectively. Here are five key points to take into account.
1. Display and Calculation Function
Types of Data Loggers
There are two primary types of data loggers to choose from
1. Models That Are Connected to a PC
These data loggers enable you to check and perform data computation on the PC display.
2. All-in-One Data Loggers
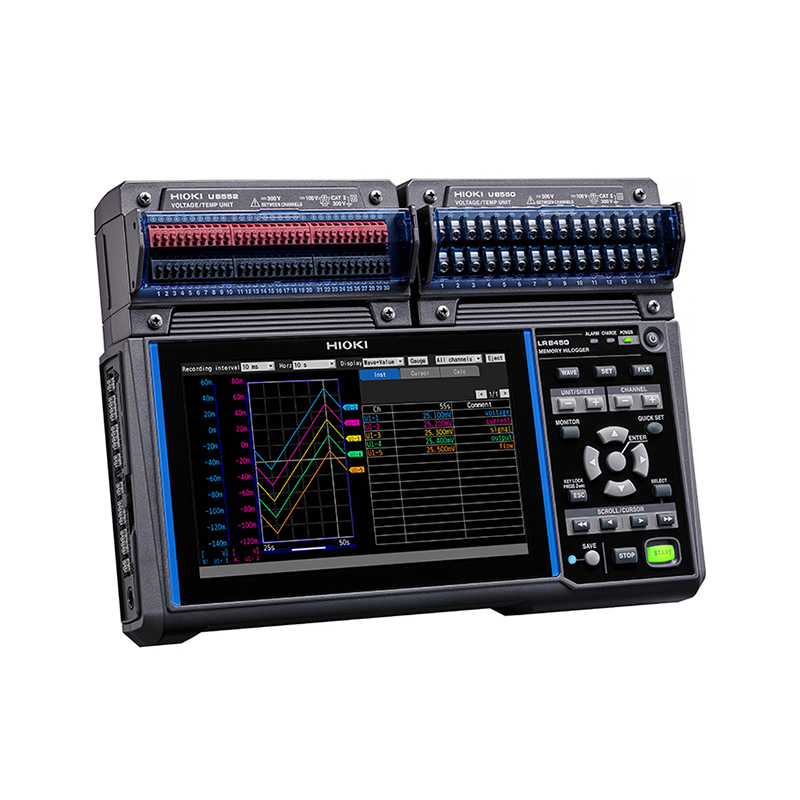
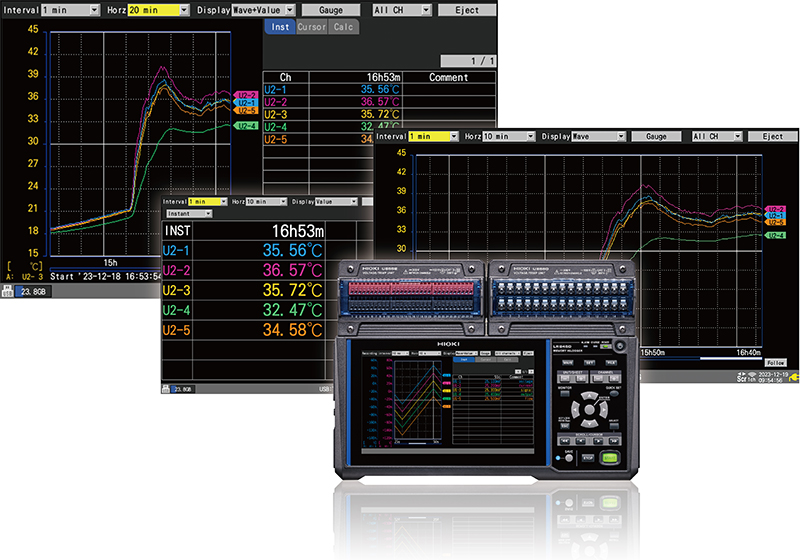
The devices come equipped with a high-resolution LCD display, enabling the setting of measurement conditions and real-time verification of recorded waveforms and numerical data.
The integrated structure of all-in-one data loggers offers increased portability and convenience by connecting the main body of the data logger to the measurement module. This setup facilitates quick identification of phenomena at the measurement site.
Display Modes and Calculations
All-in-one data loggers offer various display modes, including, waveform display, numerical calculations such as instantaneous and maximum value displays, and alarm status indications.
These multiple display options are invaluable for gaining an intuitive understanding of the phenomena occurring during data collection.
Whether you need to visualize trends, analyze peak values, or monitor alarm conditions, a data logger with diverse display capabilities can significantly enhance your ability to interpret and act upon the collected data.
2. Scalability
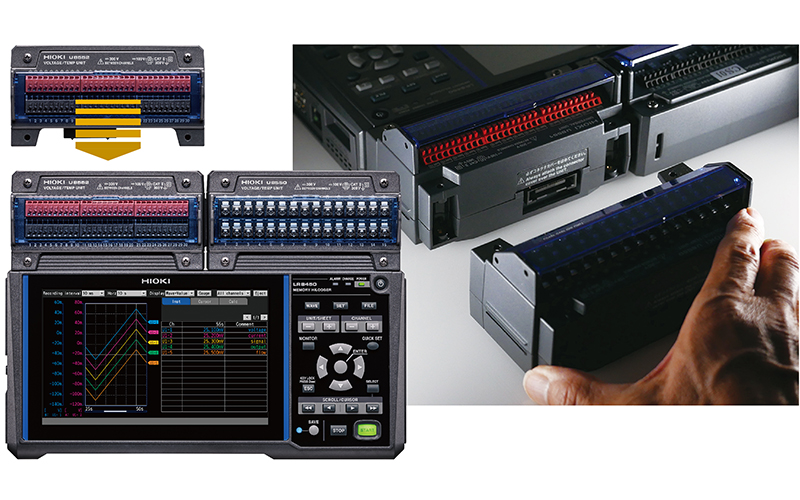
- Image of data collection of distributed measurement points by wireless measurement module, photo of data logger LR8450 with direct connection module expansion to it
Scalability is crucial when selecting a data logger, as it determines the system's flexibility and adaptability to evolving measurement needs. Here are critical aspects of scalability to keep in mind.
Wireless Communication
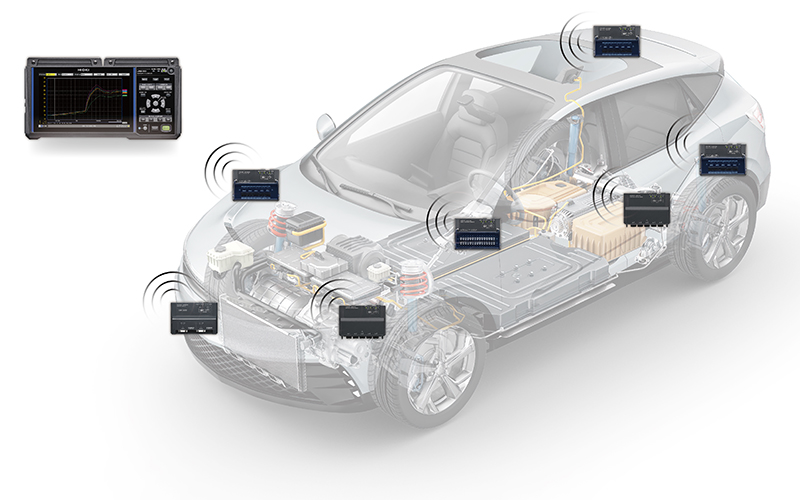
Some data loggers, such as the HIOKI LR8450-01, feature wireless capabilities. This wireless communication between the main unit and measurement modules offers distinct advantages. It is particularly effective for data collection in dispersed locations or environments where physical wiring is impractical, such as test rooms separated from control rooms.
Expansion Options
The LR8450-01 data logger supports expansion with direct connection modules (up to 4 modules) and wireless modules (up to 7). This means you can expand your data logging system to accommodate more measurement channels as your project requirements evolve.
High Channel Capacity
With the ability to add up to 330 channels, the LR8450-01 data logger provides ample capacity to handle complex measurement setups. This high channel count is especially beneficial for applications that involve monitoring numerous data points simultaneously, ensuring you can capture comprehensive data for in-depth analysis.
3. Type of Measurement
The types of measurements include temperature, humidity, voltage, current, power, strain, vibration, and more. Therefore, it's one of the important considerations when selecting a data logger. Data loggers are available in models that measure a single parameter and models that can measure multiple types. One example of a data logger that offers flexible system configuration to suit various requirements is the HIOKI LR8450-01.
Flexibility in System Configuration
The LR8450-01 allows for selection from a wide array of measurement types and enables a highly adaptable system configuration. This extensive versatility enhances its applicability to a variety of applications.
Combination of Data Logger Main Unit and Measurement Modules
The LR8450-01 data logger is used in combination with measurement modules. It comes equipped with a range of measurement modules specifically designed to work seamlessly with the data logger, allowing for easy replacement or addition as required. Next, we will introduce the measurement module to be combined with the LR8450-01.
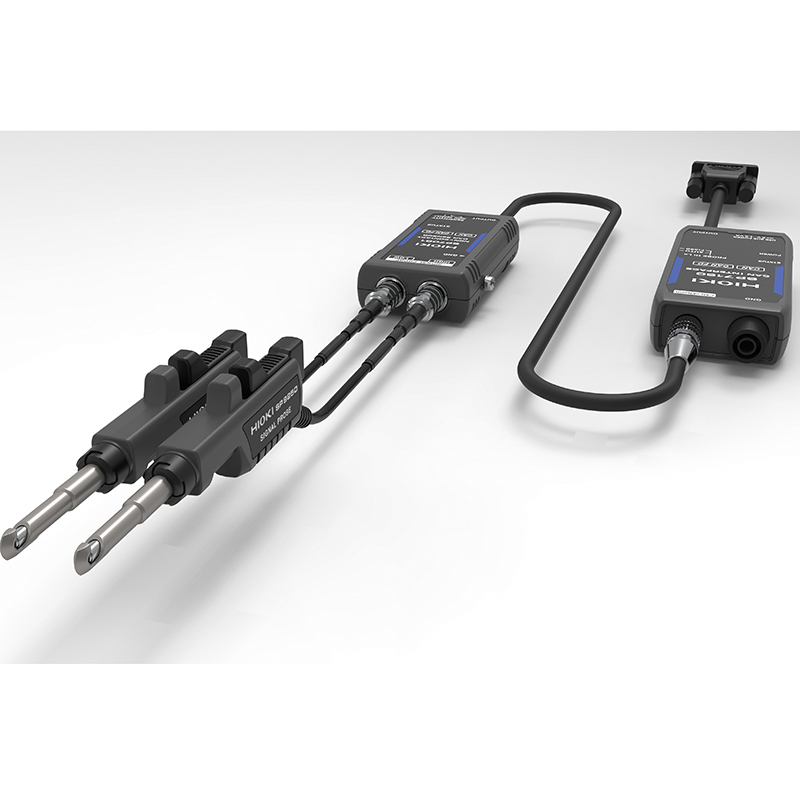
Temperature measurement (Thermocouples and Resistance Thermometers) and Voltage Measurement Modules
For temperature measurement, accurate temperature detection is achieved using either thermocouples or resistance temperature detectors, depending on the specific requirements. In the case of voltage measurement, these modules can be used for direct input within the measurement range and for input from sensors that output physical quantities such as pressure and displacement as voltage signals. There are modules available that allow you to choose between voltage and thermocouple/resistance temperature detector inputs, as well as modules that support voltage input and thermocouple inputs exclusively.
Strain Measurement Module
This module comes equipped with a bridge box, allowing for direct connection of strain gauges to the measurement module, enabling strain measurements.
Current Measurement Module
You can perform current measurements by connecting HIOKI's current sensors to this module. The current sensors you can use cover a range from leakage current to 6000A, allowing for flexible sensor selection based on your specific application needs.
CAN Measurement Module
It is a module capable of capturing CAN data, a communication protocol extensively used in various sectors, including automotive and factory automation. The module can convert CAN signals into real-time analog waveforms for display on the data logger, and it can also output recorded data as CAN signals.
User Benefits
Automotive Researchers
By incorporating a temperature measurement module, it becomes possible to monitor the temperature changes in vehicle-mounted batteries and electrical components, thereby facilitating the optimization of their design. Additionally, the use of a current measurement module allows for the collection of current consumption data. Analyzing this collected data enables improvements in energy efficiency, contributing to the development of electric vehicles with longer range.
Machine Operators
By integrating a temperature sensor module, the real-time tracking of temperature changes in equipment becomes feasible. The data logger's alarm feature simplifies setting thresholds and alarm outputs, aiding in predictive maintenance.
Employing a current measurement module allows for a detailed analysis of load currents in production equipment, helping to identify scenarios like equipment overload, thereby enhancing safety and reliability.
4. Sampling Rate
When evaluating the performance of a data logger, the sampling rate is an extremely important factor. Typically, data loggers have sampling rates ranging from tens of milliseconds to one second. The following details pertain to a sampling rate of 1ms.
Advantages of 1ms Sampling
If the sampling rate is not suitable for the rate of change in the signal being collected, there may be instances where the desired phenomena cannot be recorded. A faster sampling rate expands the range of phenomena that can be recorded by the data logger. For example, with a 1ms sampling rate, it's possible to record outputs from various sensors, such as pressure and vibration, that have frequencies in the ten Hertz range.
Key Features of Hioki Data Logger LR8450
The measurement modules that can be combined with the Hioki Data Logger LR8450 achieve 1ms sampling with high-speed voltage units and strain units. This enables high-speed and high-precision data collection of behaviors such as stress, pressure, and strain, meeting the requirements of high-speed sampling rates.
Data refresh interval can be set for each module
The LR8450 allows for setting different data refresh intervals for each measurement module, enabling simultaneous measurements.
This feature enables high-speed control signals to be measured with a data refresh interval of 1ms, and for slower changing signals like temperature, which are more susceptible to noise, a stronger filter can be applied with a 1s refresh interval. This results in highly precise measurements.
5. Safe Measurement with High Withstand Voltage
Safe measurement is paramount when working with electrical systems, and high voltage withstand specifications are crucial in ensuring safety. Here, we highlight the importance of safe measurements with high withstand voltage:
- Risks of Instrument Damage: There is a risk of instrument damage due to excessive voltage levels when using instruments without high withstand voltage specifications.
- Risk to the Operator: Elevated voltage levels can pose a danger of electric shock to the measurement operator.
- Short Circuit Between Terminals of the Object: Excessive voltage levels can lead to short circuits between the terminals of the object being measured, such as a battery pack.
- Potential for Explosions: In extreme cases, the risk of explosions or other hazardous incidents may arise when high voltages are not adequately managed or isolated.

- Wireless Module maesurement Image
- When Combined with a PC: When combining a logger with a PC, the data collection device is set up at the measurement site to record data. Afterwards, the device is taken back to a desk with a PC, connected to the PC, and the data is reviewed using dedicated software.
Alternatively, a PC can be set up at the site and the data stored directly on the PC. In this case, the reliability of the measurement depends on the PC. - Benefits of Display: All-in-one loggers with screens offer several benefits, including
- Easy-to-Read and Understand Display: The display on all-in-one loggers is designed to be user-friendly, making it easy to interpret measurement data.
- Monitoring Alarm Conditions: Users can quickly identify alarm conditions and take necessary actions when they occur.
- Instantaneous and Maximum Value Viewing: Important data points, such as instantaneous and maximum values, can be conveniently checked on a single screen.
- Visualization of Waveform Changes: The ability to view waveform changes in real time provides valuable insights into the measurement process.
- User Benefits: Using loggers with screens enhances the data collection by providing a user-friendly interface that ensures data can be reviewed and analyzed conveniently on-site.
- Simultaneous Display of Analog Data and CAN Data (Input): It allows for the concurrent display of waveforms from actual analog data, such as voltage, temperature, and strain, along with information from the CAN bus, like vehicle speed.
- Integration of Analog Data into CAN Data on Existing Systems: The HIOKI data logger "LR8450 and CAN Measurement Module" allows for centralized management by outputting the analog data it measures as CAN signals, integrating this data into the information on the CAN bus and existing systems.
- Output of CAN Signals as Alarms in Case of Abnormalities: HIOKI Data loggers "LR8450 and CAN Measurement Module" can output CAN signals as alarms when abnormalities are detected, providing valuable information for appropriate actions.
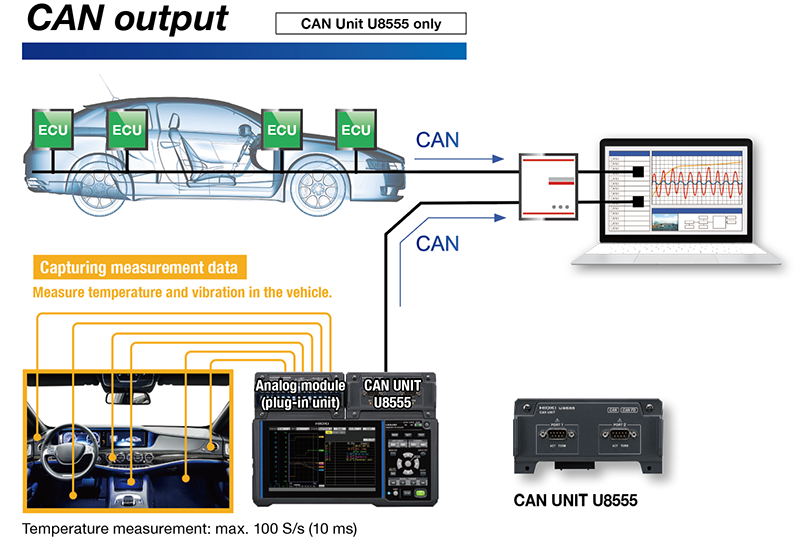
- Send analog data measured using a plug-in module over a CAN bus
Benefits of High Withstand Voltage Specifications
High withstand voltage specifications enable safe measurements in various scenarios, offering protection against potential electrical hazards. These specifications encompass features such as Maximum rated terminal-to-ground voltage, Maximum channel-to-channel voltage, and complete channel insulation.
High withstand voltage specifications are critical for mitigating these risks, ensuring the safety of both measurement equipment and personnel during electrical measurements
Common Problems that Occur During Measurements
Increased Wiring Time and Cost
Wiring can be time-consuming and costly aspect, especially when setting up a data logger in scenarios involving multiple channels or when the measurement points are distributed in various locations.
Here are some key points related to the increase in wiring time and cost:
Tedious Wiring for Multiple Channels
When the measurement points are located in separate experimental facilities, there is a need to route long wires for multiple channels. This process can be labor-intensive and time-consuming.
Time-Consuming Wiring Work
The wiring work for measurement cables between the measuring instrument and the measured object can take time, leading to delays in the setup process.
Costs of Extended Wiring
In addition to the time involved, a cost is associated with purchasing extended lengths of thermocouple sensors used for temperature detection, adding to the overall wiring component expenses
Risk of Wiring Trouble
Even if the wiring is completed, there is a risk of unexpected issues such as "The wire moved during the experiment and got disconnected." As a result, data collection may be interrupted, potentially leading to the loss of valuable data collection opportunities.
Solving with Wireless Modules
One solution to these challenges is the use of wireless modules. These wireless measurement modules are installed near the measurement target and connected without the need for wiring. By wirelessly communicating with the data logger main unit, data collection can be achieved, reducing the need for long test leads.
Noise interference
Stable Measurements Even at High Voltage and High Frequency
In data loggers, temperature measurements in noisy environments can sometimes be affected by high-frequency interference, causing shifts or significant fluctuations in the readings, making accurate measurements difficult. However, thanks to years of experience in data logger design, the LR8450 effectively mitigates the impact of high-frequency noise, ensuring stable and reliable measurements.
Wireless connection between measurement modules and the data logger main unit
To ensure the accuracy of measurements, it is advisable to establish a wireless connection between the measurement modules and the data logger body. This method effectively mitigates the impact of noise on measurement values. By adopting a wireless setup, the reliance on long thermocouple wiring, which is often vulnerable to noise interference, is significantly reduced. This approach enhances the integrity of the data collected and simplifies the measurement process.
Inability to Verify Data On-Site
The advantages of loggers with screens (all-in-one loggers that allow on-the-spot waveform viewing) have yet to be fully communicated, and PC-based loggers are predominantly used.
What is Automotive Data Logging?
Automotive data logging refers to collecting and analyzing data related to a vehicle's operations, performance, and various sensor inputs. This section will focus on the importance and applications of data logging in the automotive industry.
CAN Input & CAN Output
When there are parameters that are difficult to measure within the vehicle's condition, leveraging data from the CAN bus allows us to comprehend the state of the vehicle.
Here are the key features of CAN input and CAN output.
Customer Testimonials
The measurement process has been simplified
A major Japanese automaker overcame wiring complexities in their chassis dynamometer testing lab by adopting Hioki's LR8450-01. This wireless data logger facilitated real-time data review, eliminating the need for repeated tests and streamlining processes.
The LR8450-10 has a broad temperature range and noise resistance and is able to wirelessly connect to seven modules, collecting temperature and voltage data efficiently. The successful six-month deployment prompted consideration for additional instruments, showcasing the LR8450-01's reliability and efficiency in enhancing testing procedures.
Helped improve the energy efficiency of EVs
The key elements in xEV development are optimizing the efficiency of motors and inverters and integrating data. Temperature monitoring significantly affects the range, and data management improves operational efficiency. The success in enhancing EV performance and extending range hinges on precise temperature control and data analysis.
Hioki Products
Conclusion
The requirements for a data logger are diverse. The HIOKI data logger LR8450, with its expandable channels and various measurement modules, allows for flexible system configurations to cater to different data collection needs. This is explained using an all-in-one data logger with a display, combined with wireless measurement modules, to facilitate easy installation and wiring on-site. The wide applicability of these loggers, ranging from research and development to manufacturing settings, is also discussed. Please contact us for any measurement problems you would like to solve or if you are interested in learning more about our equipment. We are here to assist you.