Data Loggers Explained: A Beginner's Guide
Data loggers are utilized in various situations, and due to their versatility and effective data collection capabilities, they have become an essential tool in many fields. This article will explain how data loggers function in different situations and how to use them.
Common Applications for Data Loggers
This section introduces multiple applications, from measuring the temperature of individual components to measuring various parameters like voltage, current, temperature, strain, etc and multi-channel measurements. We will reveal how data loggers can be helpful in your workplace.
Objective Setting
- Data Logger LR8450-01 image
The Role of Data Loggers
Data loggers are crucial tools for precise measurement and data collection. Their uses are diverse, ranging from measuring the temperature of individual parts to multi-channel measurements of several parameters simultaneously, such as the voltage, current, temperature, and strain. Accurate data is essential for product quality assurance, process optimization, diagnostics, and research and development.
The Purpose of Data Collection
To maximize the use of data loggers, it is essential first to clarify the purpose of data collection. Depending on the purpose, many channels, various measurement targets, high measurement accuracy, fast sampling speed, and large recording memory may be required. It is vital that the phenomenon to be recorded can be accurately captured and that data can be stored for the necessary period.
How to Use Data Loggers
Selecting the Number of Channels
The selection of the number of channels in a data logger is closely related to the measurement targets and the purpose of data collection. Choosing the appropriate number of channels can enhance the simultaneity and efficiency of data collection.
- Temperature measurement of individual parts: A few channels are sufficient for such simple measurements. You use one or a few temperature sensors to monitor the temperature of specific parts or points.
- Simultaneous measurement of voltage, current, temperature, and strain in batteries: To measure these parameters simultaneously. Multi-channel measurements are essential, especially in complex systems such as electric vehicles or advanced electronic devices. This allows understanding of the correlation between different parameters and assessing the system's performance.
- Consideration of memory capacity: When using multiple channels, sufficient memory capacity is needed to store collected data. A large memory capacity is essential, especially when collecting data at high frequencies or over long periods.
Choosing Measurement Elements
When measuring only temperature
The first consideration is the range and required accuracy. Based on this, the appropriate sensor is chosen. Commonly used temperature sensors include thermocouples and resistance temperature detectors (RTDs). These have different characteristics in terms of temperature range and tolerance.
When choosing a thermocouple, it's essential to select the type (e.g., K-type, J-type, E-type, T-type) based on the characteristics of the measurement target. Each type of thermocouple has different temperature ranges and responsiveness.
When measuring different parameters simultaneously or multi-channel measurement
- Checking the type and number of measurement elements:
- Identifying elements: When measuring multiple parameters simultaneously, the first step is identifying the types and number of elements you want to measure. Depending on the measurement target, this can include various elements such as temperature, voltage, current, and strain.
- Diversity of measurement elements: Monitoring multiple parameters simultaneously enables a comprehensive system understanding, leading to more advanced analysis and responses.
- Supporting capabilities: Verify whether the chosen data logger supports all the necessary measurement elements simultaneously. This includes whether each channel is compatible with different types of sensors.
- Consider the number of channels: Consider whether the data logger has enough channels to cover all required parameters. This directly impacts the simultaneity and efficiency of data collection.
Checking the capabilities of the data logger:
- Selecting the appropriate sensor: Choose suitable sensors for each element you want to measure. For example, thermocouples or RTDs are needed for temperature measurement, voltage output converters for voltage measurement, and strain gauges for strain measurement.
- Setting the range: Set the appropriate measurement range for each element. This is important to ensure accurate data collection and enhance analysis reliability.
Setting sensors and ranges for each element:
Sampling
Sampling is essential when collecting data with a logger. The sampling interval must be chosen appropriately based on the change speed in the observed phenomenon.
- Sampling in cases of rapid change: For example, sampling at a 1 ms interval can be essential for capturing sudden changes and recording the outputs of various sensors. This is particularly useful for testing and experimenting with automotive brakes, strain in piping, hydraulic pressure in construction machinery, and stress and load on moving parts of industrial robots.
- Sampling in cases of slow change: For phenomena that change relatively slowly, such as temperature and humidity, sampling at 1-minute intervals is suitable. Such cases include measuring temperature and humidity differences in rooms or monitoring the energy usage of buildings and facilities.
Setting Recording Time
It's important to set the data logger's recording time properly based on the sampling speed and the number of channels.
When there are many channels, and the sampling speed is fast, such as several milliseconds, a large amount of data is generated, requiring appropriate memory capacity. The longer you set the recording time, the more memory capacity is needed.
Also, consider the sampling speed and measurement channels when determining the recording time. Especially in cases of long-term monitoring or when a large amount of data is expected, attention should be paid to the method and frequency of data storage.
- Measurement Target Infographic
The Overall Process of Measurement
The measurement process using a data logger consists of a series of steps. Understanding and properly managing this process ensures the quality and reliability of data.
Basic steps of measurement:
1. Start recording:
Set up the data logger and start measuring.
2. Data collection:
Data is collected according to the selected sampling interval and channel settings. In the case of data loggers with a display, you can check the data on the logger itself.
3. Stop recording:
Stop the data logger's recording at the end of the measurement.
4. Data analysis on PC:
Transfer the collected data to a PC and analyze it.
- Optimizing the sampling interval: To capture changes over a short period, it's necessary to set the appropriate sampling interval.
- For manual operation of recording start and stop: When collecting data at sampling intervals in milliseconds, it is required to do so at a time that does not miss the target phenomenon. For example, the Hioki data logger LR8450 offers a "trigger function" that allows you to start and stop measurements based on specific conditions or signals.
Points to note when setting up for measurements:
Uses of Data Loggers
Measurement of Component Current and Temperature
Switching power supplies installed in electronic devices must efficiently convert commercial AC power into low-voltage DC power. Managing and minimizing thermal losses is necessary to achieve a high-efficiency power supply. The heat energy generated is directly linked to energy loss, so understanding thermal losses can help reduce the product's power consumption.
For instance, a significant amount of heat generated in the components inside electrical equipment is due to large currents flowing through them. By recording the temperature changes of parts during the operation of electronic devices with a data logger and simultaneously measuring power consumption with a power meter, you can understand the causal relationship between temperature and power consumption during operation. This data can then be used to devise strategies such as reducing current in the circuit to lower heat generation.
Hioki's Solution
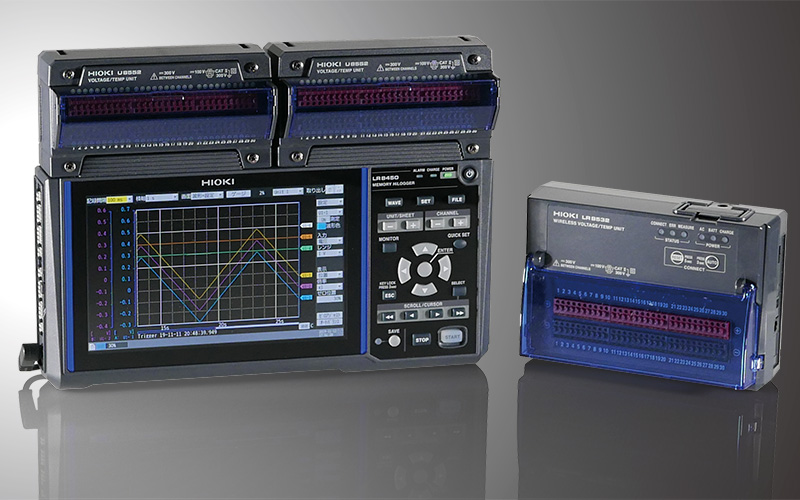
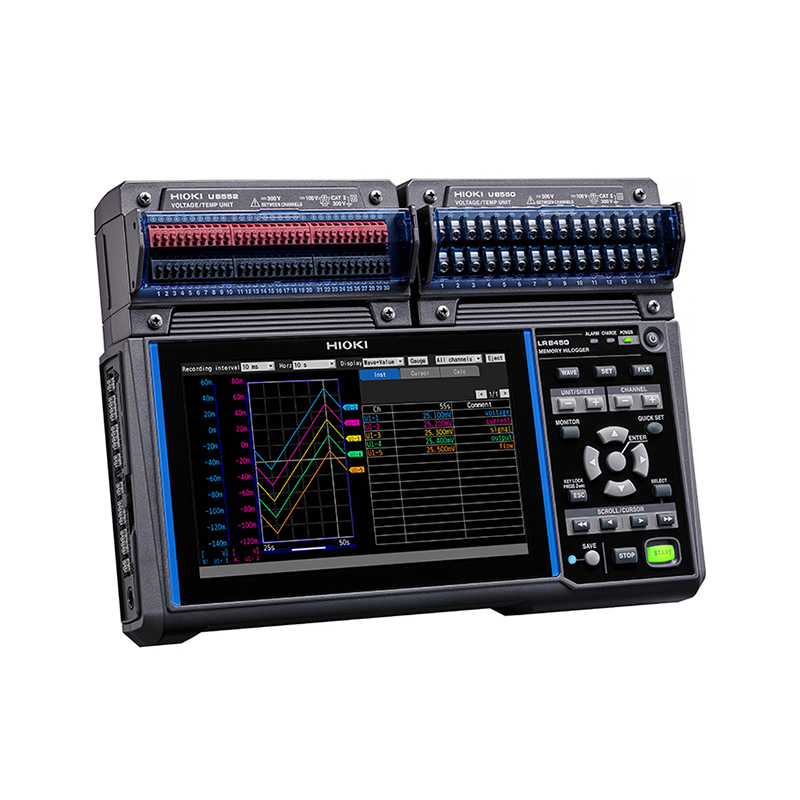
Designed for simultaneous recording of multi-point temperature data and current around power supply units, the Hioki data logger LR8450 allows a flexible combination of various measurement modules.
Its channel expandability and current input through the current module and sensor make it an ideal tool for long-term temperature and current recording for in-development products.
For more detailed information, please visit the following link.
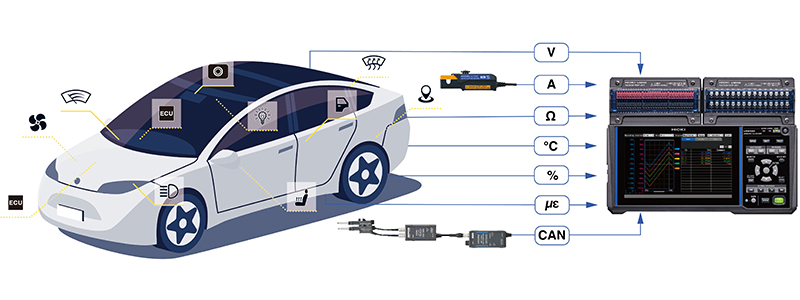
Vehicle-Wide Data Acquisition in Automobiles
Evaluating automobiles requires measurement data from different parts of the vehicle. This includes the fuse box in the front part of the vehicle, the temperature inside the cargo area, waste heat in the engine room, and the rigidity of the body and shaft, among others. However, attempting to acquire all these data simultaneously can lead to complex wiring issues.
Hioki's Solution
The Hioki data logger LR8450-01 supports wireless modules. These wireless modules are battery-operated, independent measuring units that can be placed close to the measurement targets. The data measured by each module can be transmitted wirelessly to the main body of the data logger. This reduces the need for complex wiring, thereby improving work efficiency and reducing the risk of data loss due to disconnection or noise.
Using this data logger for comprehensive vehicle data acquisition enables measurements that contribute to the power management of electric vehicles (EVs).
For more detailed information, please visit the following link.
Why Choose Hioki Data Loggers?
Thanks to their unique features and advantages, Hioki data loggers offer high efficiency and reliability in various applications.
Advantages of Data Loggers with Displays
Real-Time Data Display
The real-time data display function provided by Hioki data loggers is essential for data analysis and decision-making during measurements. This feature lets users quickly grasp data trends and adjust measurement conditions or optimize processes. In case of unexpected occurrences or anomalies during measurement, Hioki data loggers can promptly identify and notify the user. This capability enables early problem resolution and potential risk mitigation, significantly improving measurement reliability.
Ease of Configuration
Hioki data loggers feature a user-friendly interface. Users can easily make critical settings such as sampling intervals, measurement ranges, and alarm settings. This is particularly beneficial in the field and experimental processes where measurement conditions frequently change, allowing flexible adaptation to varying environmental conditions and measurement requirements.
No Need for a Dedicated PC for Data Recording
Hioki data loggers, especially the LR8450-01 model, offer an all-in-one solution that does not require a dedicated PC. Users can complete data sets, collection, and analysis with a single device, reducing the need for additional hardware or software. The lightweight and compact data loggers also make installation and movement on-site easy, contributing to work efficiency.
Wireless Measurement Modules
Distributed Installation Across Multiple Locations
Wireless measurement modules allow data collection across a broad area without the constraints of cables or wired connections, which is especially effective in environments with multiple measurement points. The LR8450-01 can collect and manage multi-channel data from each wireless measurement module with a single data logger unit. This enables efficient data collection and analysis in the same time series.
Easy Mobility and Expansion
Flexibility in Installation Sites: Wireless capabilities allow freedom in choosing the data logger's installation sites. Changing and expanding installation sites is particularly convenient in dynamic testing environments and changing research conditions. Examples include test labs and control rooms. In test environments separated by walls, the wireless function eliminates the need for additional work to pass measurement cables, reducing installation effort and costs and facilitating smooth measurement initiation.
Additional Features
Predictive Maintenance (Alarm Function)
When systems or processes enter an abnormal state, data loggers can notify users, enabling early detection of issues. This can prevent significant failures or downtime, reducing costs like opportunity loss in production lines and repair expenses.
Example:
If you want to stop a device when its temperature gets too high, the data logger can output an alarm signal when the set high-temperature threshold is reached. This output can convey the alarm occurrence to the device and control warning lights.
Utilizing Remote Operation
HTTP server function
Hioki's LR8450 data logger model can be controlled via LAN connection to an office PC. Using a standard browser, it's possible to start and stop measurements remotely and check waveforms in real-time.
Using GENNECT Cloud
Data measured by the LR8450 is transferred to Gennect Cloud and managed on their servers. This facilitates data sharing and remote access among multiple teams and departments, leading to more efficient operations. Furthermore, data backup is available, providing resilience against external incidents.
Hioki Products
Conclusion
This article thoroughly explored data loggers' various uses and advantages. Data loggers are versatile, multi-purpose tools suitable for multiple applications, from single-part temperatures to simultaneous voltage, current, temperature, and strain measurements. Identifying energy loss through monitoring consumption current and temperature is crucial in electronic device development. In developing EVs, they are indispensable in managing the entire vehicle's power. Hioki’s data loggers have met these demands with their high versatility and reliability. Discover opportunities for optimizing business efficiency from each application.