Accelerate product development for Scope 3 emission reduction
Scope 3 emission reduction through recording of current consumption and heat energy loss
To attain Scope 3 (*1) emissions targets and ensure alignment with decarbonization goals (some refer to this as achieving carbon neutrality or zero carbon status), it is important to accurately understand the impact of our products on the environment.
Looking ahead, manufacturers will likely need to clearly disclose their products' energy consumption to end-users. For engineers involved in product development, minimizing product power consumption emerges as a critical priority.
In this application note, we will offer tips to aid developers striving for Scope 3 compliance, focusing on techniques to pinpoint energy losses in electronic components through current and temperature data acquisition. As an example, we will look at measurement in switch-mode power supply (SMPS).
- *1:What are Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions?
- Scope 1: Direct emissions of greenhouse gases by businesses themselves (e.g., fuel combustion, industrial processes)
- Scope 2: Indirect emissions from the use of electricity, heat and steam used by the business and supplied by other companies
- Scope 3: Indirect emissions other than Scope 1 and Scope 2 (emissions of other companies related to the company's activities)
Background
SMPS provide a stable and appropriate power supply for electronic devices. They efficiently convert commercial AC power into low-voltage DC power. To ensure a highly efficient power supply, the management and minimization of heat loss become imperative. The direct correlation between generated heat and energy loss underscores the importance of limiting heat generation. Understanding the current consumption and heat generation of electronic components enables taking proactive steps to significantly reduce the overall power consumption of the end product. Optimizing electronic device heat loss and power consumption reduces Scope 3 emissions. Understanding heat generation and energy utilization permits proactive efforts to reduce power consumption and Scope 3 emissions.
Challenges in Reducing Power Consumption During the Product Development Process
In order to reduce the power consumption of their products, engineers encounter the following three challenges during the product development phase:
- 1.Understanding how power is consumed across different operational modes
- 2.Pinpointing energy loss areas
- 3.Keeping pace with rapid development
1. Understanding how power is consumed across different operational modes
Looking ahead, manufacturers will be required to disclose the power consumption of their products to end users. Traditionally, manufacturers measure the rated power of a product using instruments like power meters. However, since traditional power consumption specs are based on the operating mode of largest power consumption, users who calculate power consumption end up with an inaccurate and overestimated value. This predicament is why there is a growing demand for power consumption data for various operation modes. The data verifying the power consumption of the developed product in various operating modes, such as standby mode, rated operation, and overload, is valuable information for the end users of the product, and it also has the advantage of enabling quick action towards Scope 3.
2. Pinpointing energy loss areas
To minimize energy waste, simultaneous examination of interrelated data—current consumption, heat generation, and even vibration—is vital for clearer insights. For example, components that have a high current flow in electrical equipment largely contribute to heat generation. By understanding the relationship between the current value and temperature, we can take measures such as reducing the current in the circuit to decrease the amount of heat generated.
3. Keeping pace with rapid development
Engineers must swiftly conduct comprehensive reliability, durability, and destructive tests within a tight verification schedule to meet the product launch schedule. Also to adapt to the rapid changes in our world, development needs to be faster and its evaluation processes must be streamlined. This requires simultaneous recording of multiple parameters—like current and temperature—to efficiently drive assessments forward.
Recording Current Consumption and Heat Loss: Hioki's Solution for Scope 3 Emission Reduction
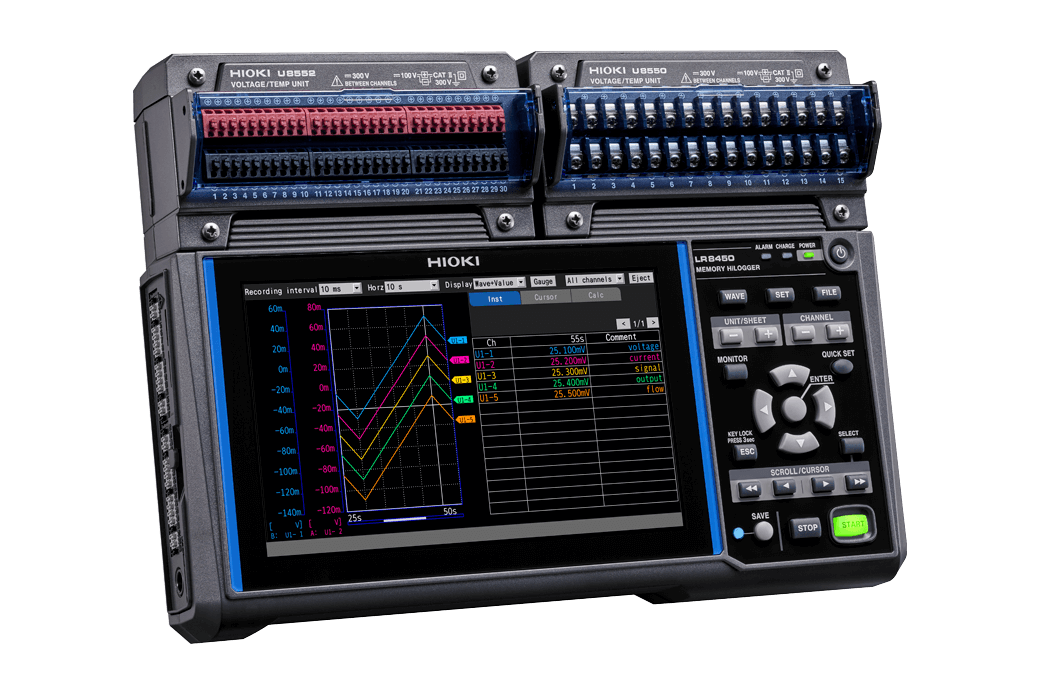
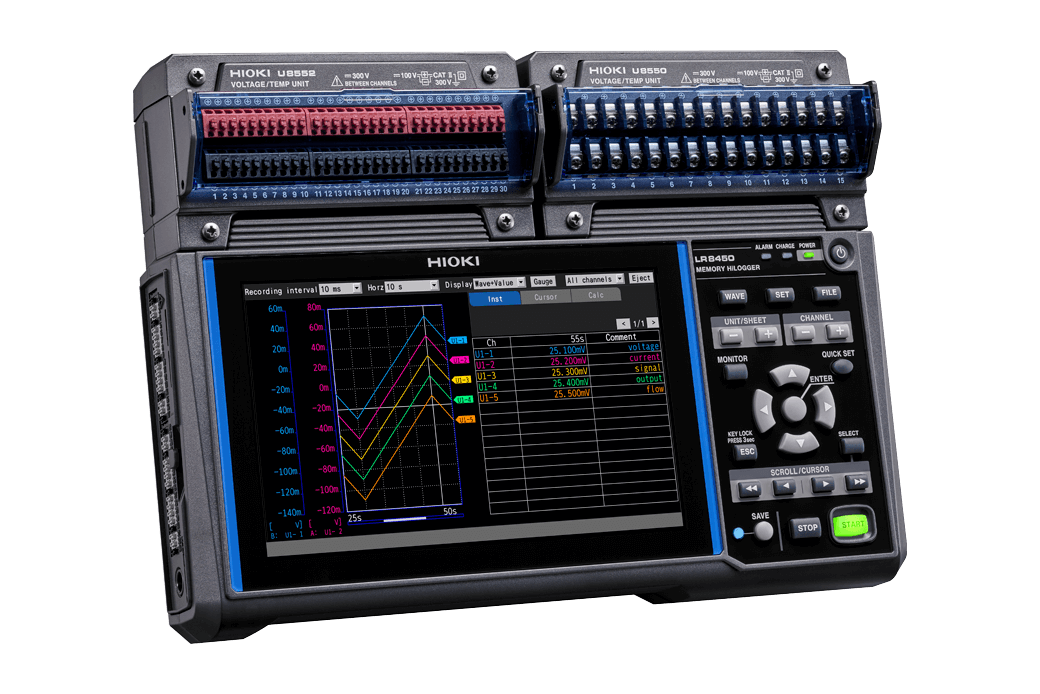
Pinpointing the causes for energy loss is not easy. However, recording and reviewing the current consumption together with the temperature of electronic components over extended periods of time can provide special insights for this task. For this, Hioki's data logger LR8450 and the small yet high-precision DC current sensor CT7812 (or CT7822) excel. The LR8450, a multi-channel data logger, captures electrical and physical parameters—current, voltage, temperature, vibration, and CAN bus data—across up to 330 channels.
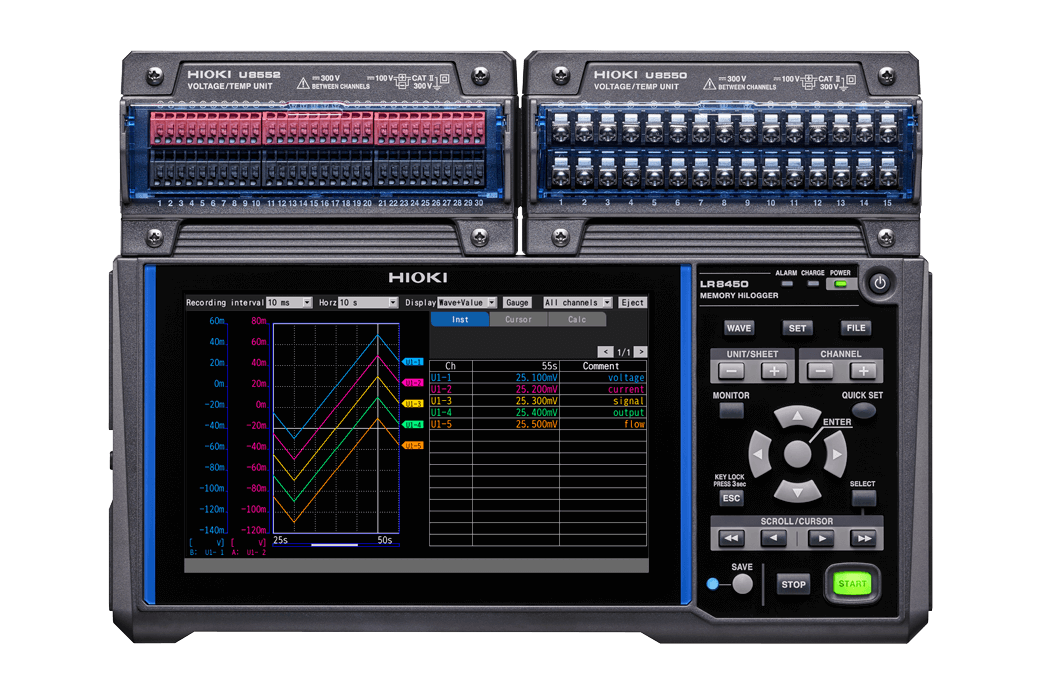 Data logger LR8450
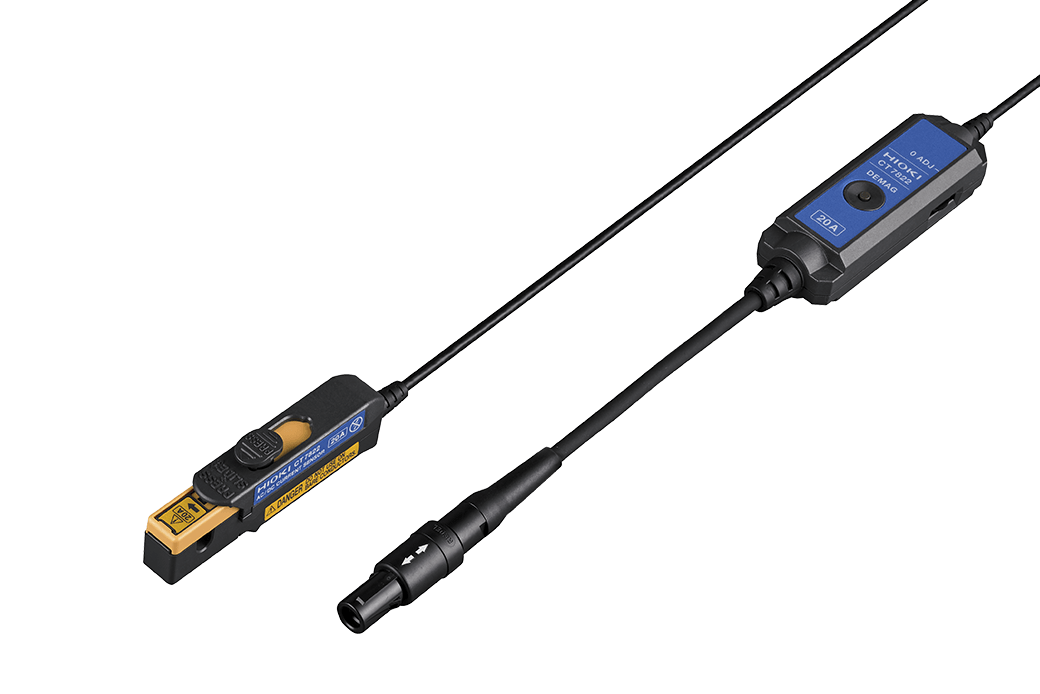
Data logger LR8450 AC/DC Current sensor CT7812
AC/DC Current sensor CT7812
The LR8450 and CT7812 (or CT7822) are ideal for this kind of application of measuring current consumption and temperature for the following reasons:
- 1.Precision in Your Grasp: High-Precision, Finger-Sized Current Sensor for Effortless Measurement
- 2.Spot Energy Waste Swiftly: Simultaneous Parameter Tracking to Detect Energy Waste Efficiently
- 3.Adaptable Measurement Solutions: Versatile Modules Tailored to Diverse Needs
1. Precision in Your Grasp: High-Precision, Finger-Sized Current Sensor for Effortless Measurement
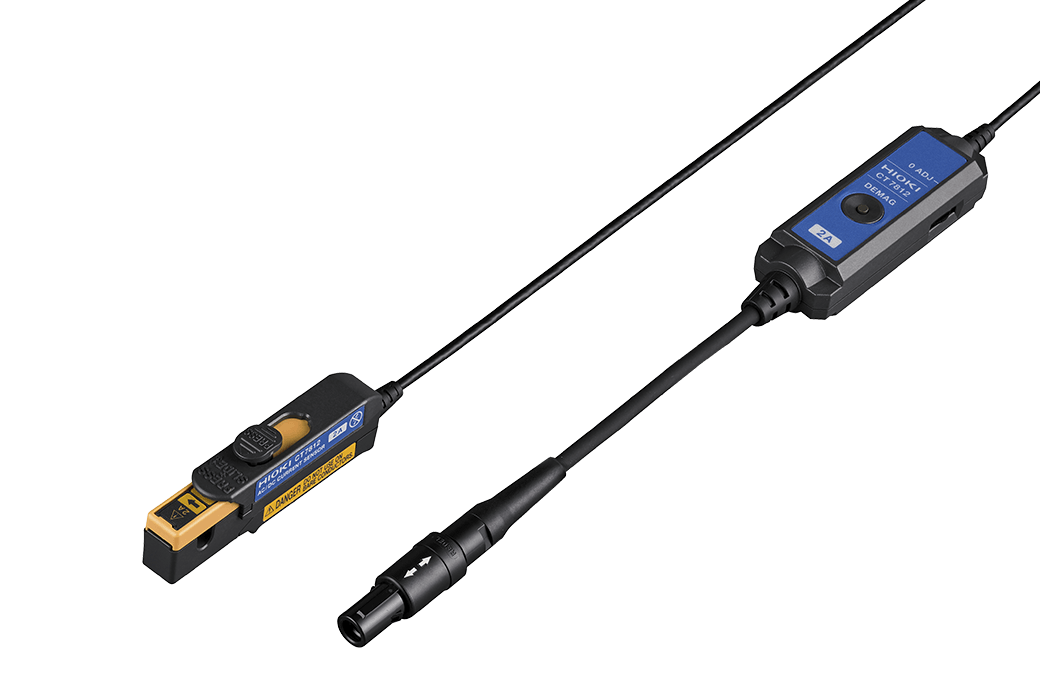
The small DC current sensors CT7812 (2 A) and CT7822 (20 A) excel at accessing confined spaces around power supply devices. To measure current, simply clamp the sensor onto a wire of the targeted device. The easy and non-invasive clamping minimizes the impact on your device's system and reduces connection time, all without modifying your device. Hioki's clamp sensors (details below) also serve well for maintenance tasks, like measuring the current usage of installed equipment. Utilizing flux gate technology, this sensor boasts minimal drift and temperature changes, ensuring long-term, precise power consumption recording.
Learn more about our current sensors' flux gate technology here
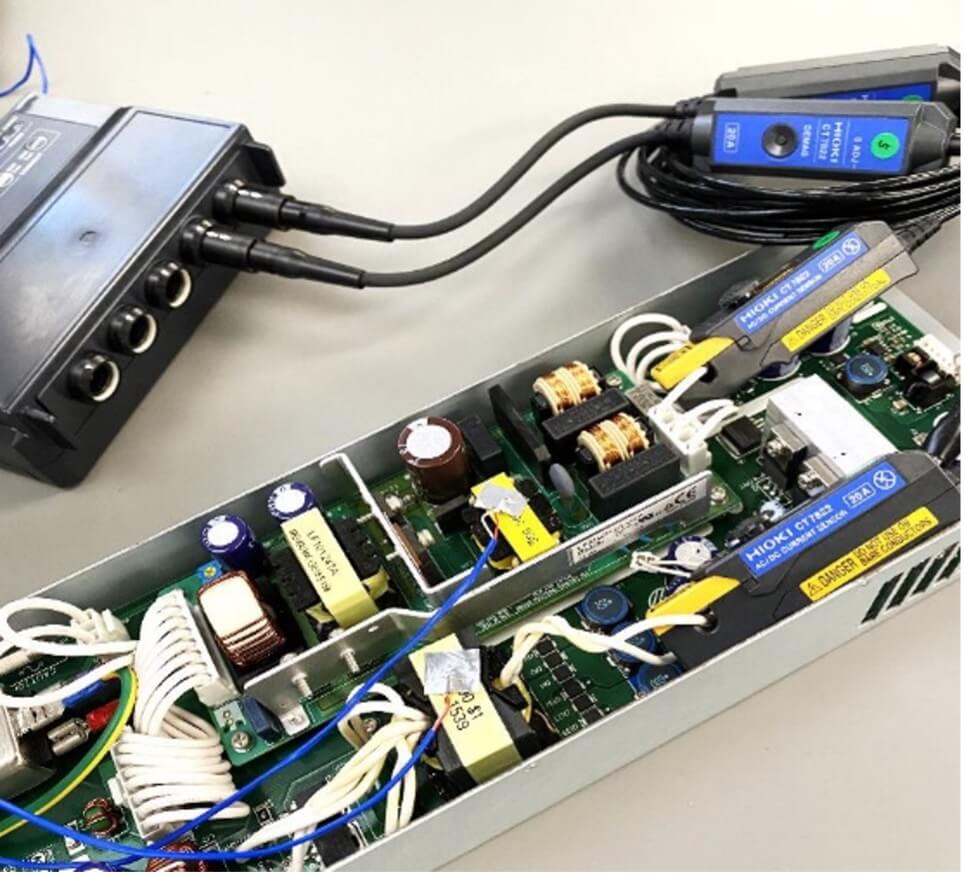

2. Spot Energy Waste Swiftly: Simultaneous Parameter Tracking to Detect Energy Waste Efficiently
Temperature and vibration measurements can effectively detect component-level losses that a current sensor cannot access. The LR8450 data logger not only facilitates temperature and heat flow measurements but also captures vibration and strain data. Simultaneously recording current consumption with temperature and vibration enables swift identification of energy losses caused by heat and vibration generation. Real-time display of recorded data expedites design verification and debugging processes. Intuitively visualizing multiple consumption-related parameters like this ensures a comprehensive assessment of energy loss factors during product development.
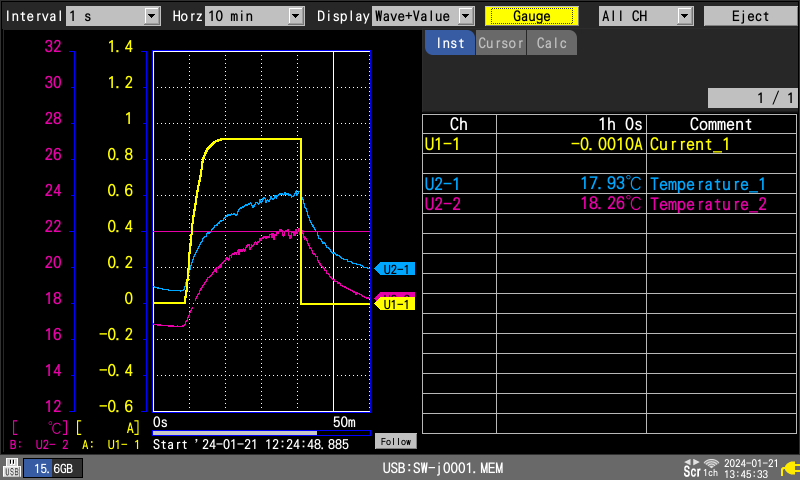
3. Adaptable Measurement Solutions: Versatile Modules Tailored to Diverse Needs
The LR8450 has seven measurement modules, supporting various signal recordings. Not only can it integrate basic recording parameters such as voltage, current, resistance, and temperature, but it can also integrate sensors with pulse and logic output, strain gauge sensors, and CAN bus measurement data. Its high expandability in measurement channels makes it useful for various evaluation purposes.

Some examples of evaluation tests where the LR8450 is useful:
- Temperature Cycle Test: recording the measurement target's temperature with high precision using Pt-type temperature sensors
- Cable Bending Durability Test: monitoring and recording the wiring resistance of the cable used in your product
- Battery Nail Penetration Test: recording sudden voltage and temperature changes with high-speed 1 ms sampling intervals
- Large-Scale Heat Test: recording temperature data in more detail (up to 330 channels) to verify the thermal design of your product
Product used for current and temperature recording
Fig. 1 shows an example of the products used for measuring the current and temperature of components in electronic equipment. For current measurement, there are two types of modules: the direct connection type U8556 and the wireless type LR8536. Both modules allow you to connect to up to five current sensors. The LR8450 automatically recognizes the connected current sensor's model and converts the measurement result into the appropriate current scale for display, eliminating the need for equipment setup. The voltage/temperature modules U8550 or LR8530 (wireless) can measure temperature using a thermocouple as the temperature sensor.

Fig. 1: Example of products used for this application
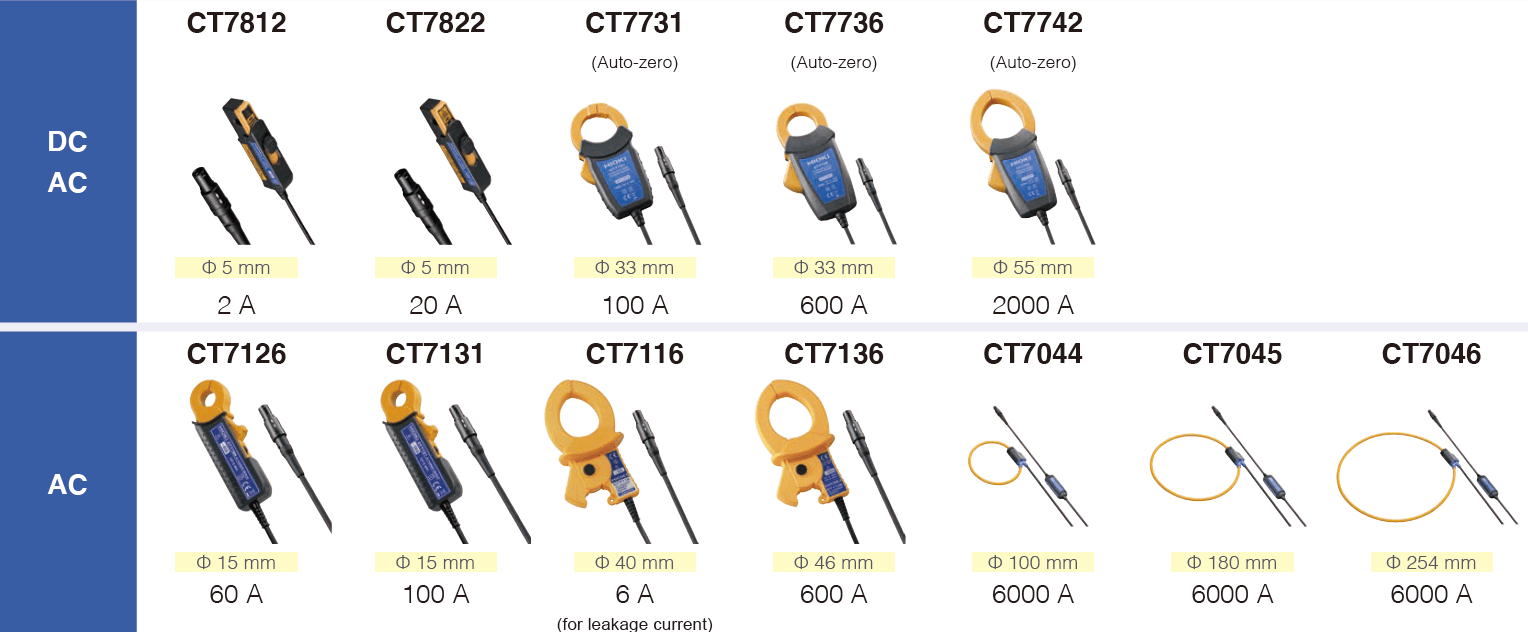
Table 1 presents Hioki's current sensors that are compatible with the LR8450. Hioki offers a variety of sensors that match specific application demands such as the current level and diameter of the wire.
Table 1: List of current sensors compatible with the LR8450
| Product | Type | Current | Diameter of measurable conductors | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT7812 CT7822 | Small and high-precission AC/DC | 2 A 20 A | φ 5 mm | Current measurement of electronic components in electrical devices and EVs |
| CT7731 CT7736 | Auto-zero AC/DC | 100 A 600 A | φ 33 mm | Current measurement of inverters |
| CT7742 | Auto-zero AC/DC | 2000 A | φ 55 mm | High-current measurement og inverters |
| CT7126 CT7131 | AC | 60 A 100 A | φ 15 mm | Current measurement of commercial power supplies |
| CT7116 | AC | 6 A | φ 40 mm | AC leakage current measurement |
| CT7136 | AC | 600 A | φ 46 mm | Current measurement of commercial power supplies |
| CT7044 CT7045 CT7046 | AC | 6000 A | φ 100 mm φ 180 mm φ 254 mm | Current measurement of commercial power supplies |
Finally
Manufacturers in the electronics industry are proactively working to reduce greenhouse gas emissions across the entire lifecycle of their products—during production, sales, usage, and disposal. Hioki's LR8450 data logger, combined with its current sensors, plays a pivotal role in visualizing critical energy loss data, including current consumption, heat, and vibration. This visibility marks an initial stride toward energy-efficient design for developers. For deeper insights into the LR8450, explore our product details. Also please reach out to us for product demonstrations or consultative discussions on applications and solutions. Together, let's advance towards a greener and more sustainable electronic landscape.